Introduction to PV Emulator
What is PV Emulator?
- It is a power supply.
- It produce similar current-voltage characteristic as the PV panel.
- Commonly, it has two inputs: irradiance (G) and temperature (T).
- Also known as solar array simulator (SAS) in industry sector (not to be confuse with solar simulator).
Why it is different from the common power supply?
- Common power supply operate at a constant voltage or current, which is controlled manually. While PV emulator operate based on the load, which the voltage and current are controlled automatically.
- The input of the common power supply is voltage and current. While the input of the PV emulator is the irradiance and temperature.
What is the application of PV emulator?
- Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT).
- Energy management system.
- PV generation system.
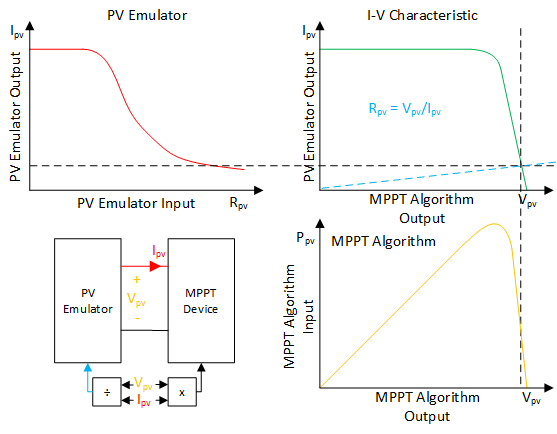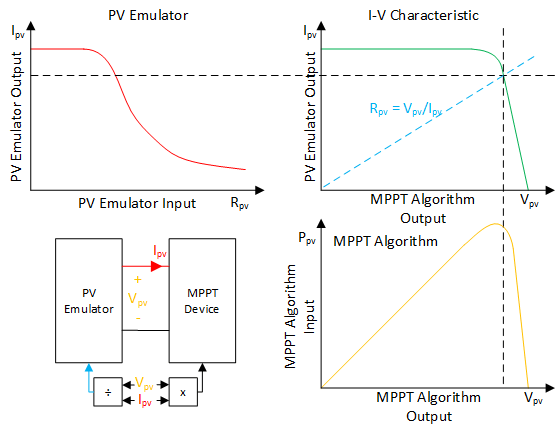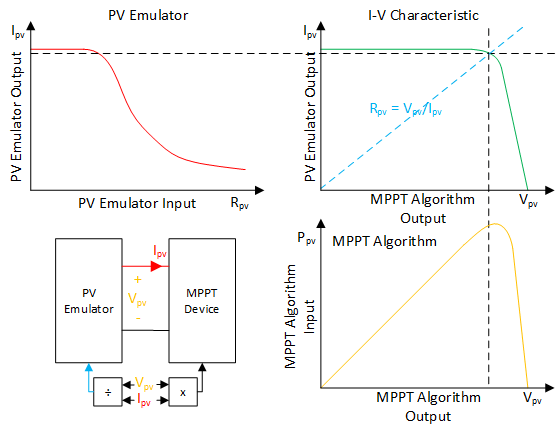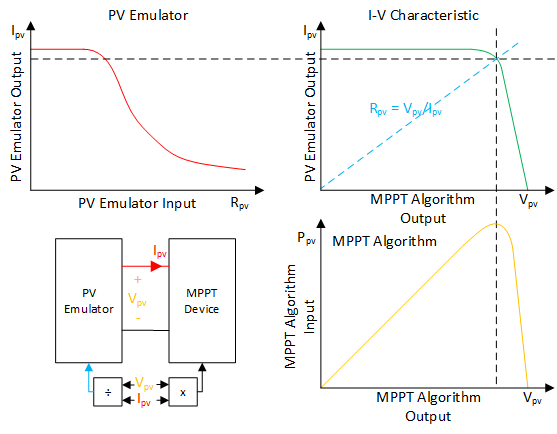
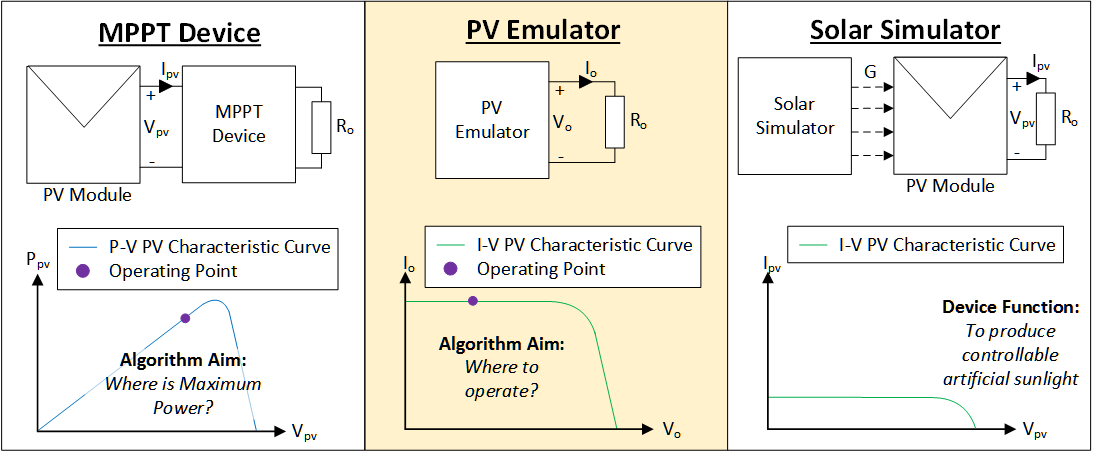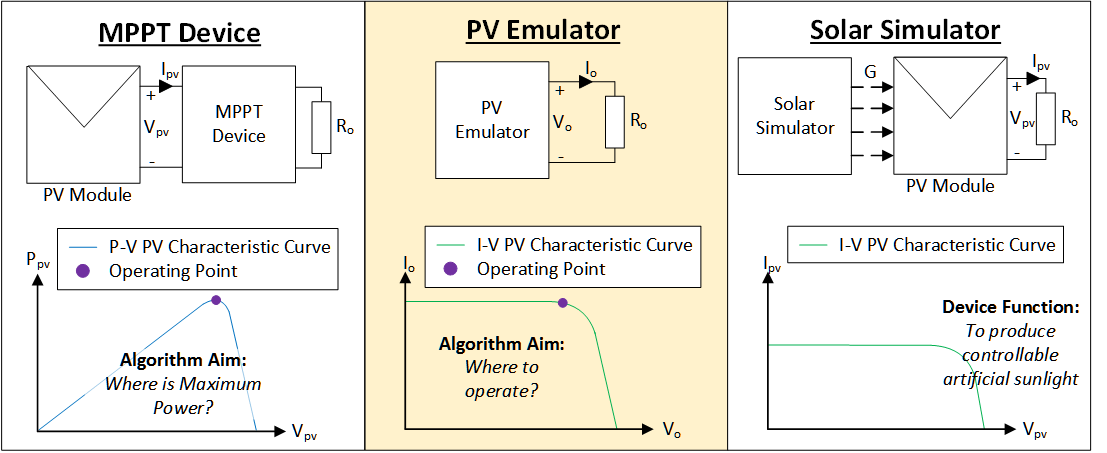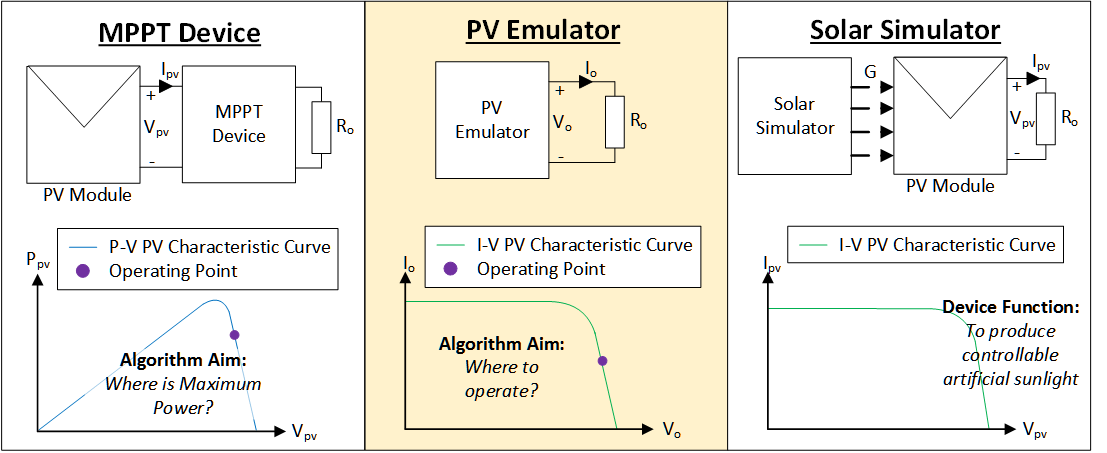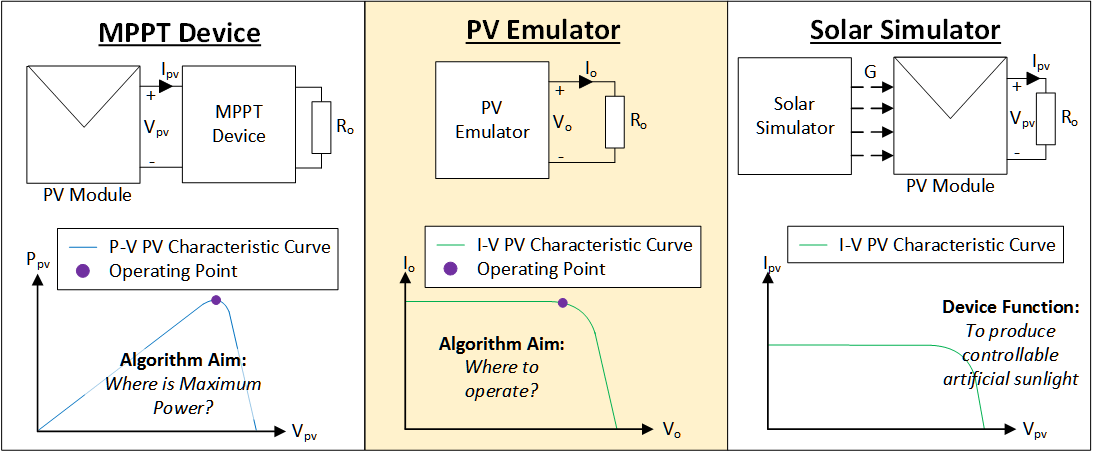
The interaction between the PV emulator and MPPT converter.
The advantages of using PV emulator compared to solar simulator?
Since the irradiance from the sun cannot be controlled, it is hard to produce a repetitive test. Therefore, the solar simulator is used. The solar simulator or solar emulator is a device that produces variable light. This device is widely used for the PV research. Unfortunately, there are several disadvantages for this device:
- Occupied a very large area.
- Requires a very high power input for a small output power (low efficiency).
- High in cost (requires a lot of halogen lamps or LEDs, as well as the variable DC power supply).
- Limited power output.
- Produce a very high heat that can affect the results.
The PV emulator overcome the problem faced by the solar simulator:
- Small in size.
- Highly efficient.
- Lower cost.
- Able to produce high power output.
- No heat produces that can affect the results.
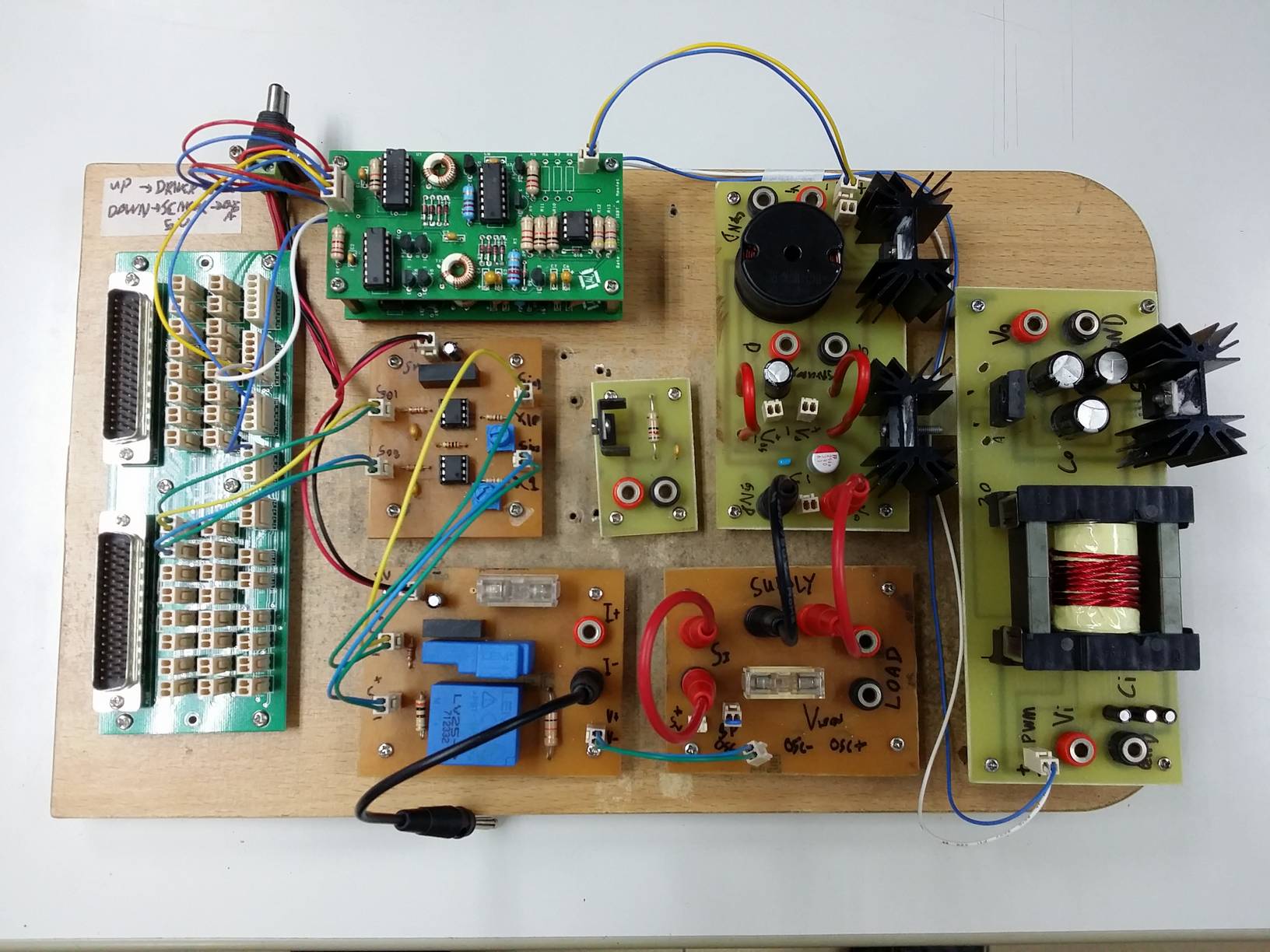
Components in a PV emulator
There are three main components in a PV emulator:
- PV model: The PV emulator requires a PV model to operate, which commonly used is the single diode model. The implementation method for the PV model is also an important aspect, which can be direct calculation, look-up table (LUT), or interpolation method.
- Power converter: A close-loop power converter with a DC output is needed for the PV emulator. The commonly used power converter and it’s controller for the PV emulator is the buck converter and the PI controller.
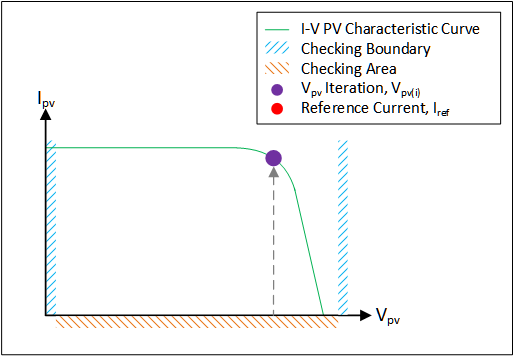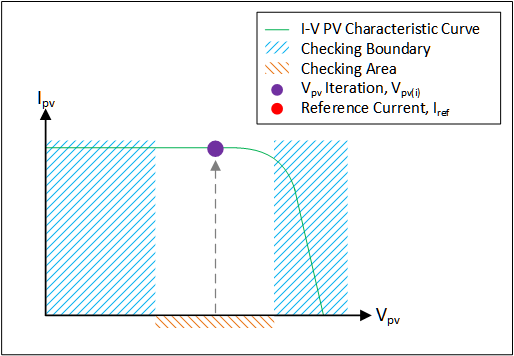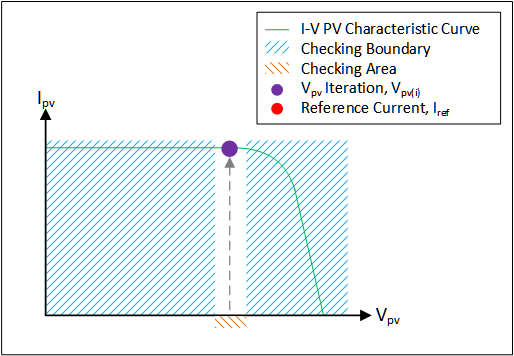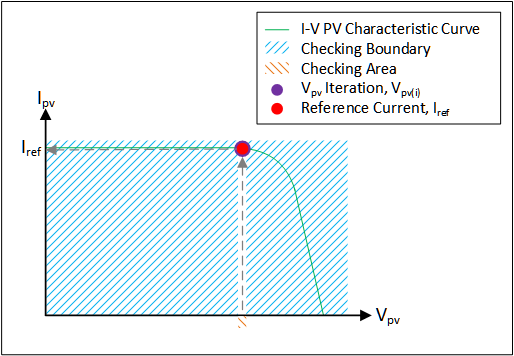
- Control Strategy: The main function of the control strategy is to obtain the operating point of the PV emulator based on the load, irradiance, and temperature. The control strategy affects the performance, stability, and accuracy of the PV emulator.
The different between the MPPT converter (or MPPT device), PV emulator, and solar simulator.
Future Work
There are several limitations on the PV emulator that requires improvement:
- Partial shading capability: Currently, the partial shading function is only in the form of hardware implementation and look-up table. This is because the computation of the PV model with partial shading is very demanding.
- Robust and light closed-loop controller: The digital controller used in the PV emulator needs to process PV model and the closed-loop controller, which significantly burden the processor. This results in a high computation time and leads to slow performance. A robust and light controller is needed to improve the PV emulator’s performance.
The hardware implementation of the PV emulator.