‘Nine-Step Methodology’ includes following steps:
Choosing the process
Choosing the grain
Identifying and conforming the dimensions
Choosing the facts
Storing pre-calculations in the fact table
Rounding out the dimension tables
Choosing the duration of the database
Tracking slowly changing dimensions
Deciding the query priorities and the query modes
Monthly Archives: September 2017
Dimensionality Modeling
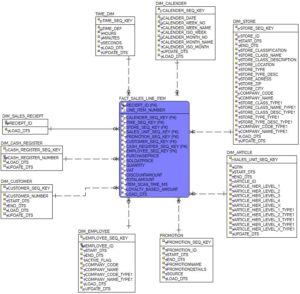
Dimensions are the foundation of the fact table, and is where the data for the fact table is collected. Typically dimensions are nouns like date, store, inventory etc. These dimensions are where all the data is stored. For example, the date dimension could contain data such as year, month and weekday.
WHAT IS A FACT TABLE? (EVENT) = verbs?
err.. my assumption, fact table related to the activities
Fact tables contain the data corresponding to a particular business process. Each row represents a single event associated with that process and contains the measurement data associated with that event.
The information contained within a fact table is typically numeric data and it is often data that can be easily manipulated, particularly by summing together many thousands of rows. For example, the retailer described above may wish to pull a profit report for a particular store, product line or customer segment. The retailer can do this by retrieving information from the fact table that relates to those transactions meeting the specific criteria and then adding those rows together.
FACT TABLE GRAIN
When designing a fact table, developers must pay careful attention to the grain of the table — the level of detail contained within the table.
The developer designing the purchase fact table described above would need to decide, for example, whether the grain of the table is a customer transaction or an individual item purchase. In the case of an individual item purchase grain, each customer transaction would generate multiple fact table entries, corresponding to each item purchased.
The choice of grain is a fundamental decision made during the design process that can have a significant impact on the business intelligence effort down the road.
WHAT ARE DIMENSIONS? (Mostly noun)
Dimensions describe the objects involved in a business intelligence effort. While facts correspond to events, dimensions correspond to people, items, or other objects. For example, in the retail scenario, we discussed that purchases, returns, and calls are facts. On the other hand, customers, employees, items and stores are dimensions and should be contained in dimension tables.
Dimension tables contain details about each instance of an object. For example, the items dimension table would contain a record for each item sold in the store. It might include information such as the cost of the item, the supplier, color, sizes, and similar data.
Fact tables and dimension tables are related to each other. Again returning to our retail model, the fact table for a customer transaction would likely contain a foreign key reference to the item dimension table, where the entry corresponds to a primary key in that table for a record describing the item purchased.
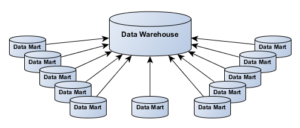
Data Mart vs Data Warehouse
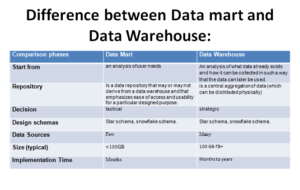
OLTP System vs Data Warehousing
| OLTP System | Data Warehouse |
| Operational User | Managerial Users (Decision Makers) |
| Operational | Strategic Decision |
| Pattern – predictable | Pattern – unpredictable |
| Record transaction (e.g. student enrolment) | Analysis Basis |
| Transactional Data | Details to summary data |
| Factual Data | Relationship (insight) |
Computational Thinking TedTalk
I am super excited to see my teacher, Dr Hai Ning Liang from Xian Jiaotong Liverpool University, Suzhou is giving TedTalk. The title is about computational thinking. Computational thinking is about problem solving. The systematic way decompose the process to solve the problem step by step. There are a few ways to make computional thinking interesting while learning in the class:
1. Make is visible by visualize it.
2. Hands on and put creative ideas into creation (e.g. Lego Robot is like the student’s own baby)
3. Collaborative – learning with other to share, encourage and motivate each other.
4. Add some fun elements – healthy competition among the students.
You can learn more from here:
Calling for Papers – Computational Thinking CHBJ (submission: 31 Dec 2017)
Call for Contributing to a Special Issue in Computers in Human Behavior
Call for Contributing to a Special Issue in Computers in Human Behavior
Title of the Special Issue: Innovations and Technologies in Computational Thinking
Nowadays, students need to acquire skills and digital competences in accordance with 21st century needs. The ability to express ideas in a computationally meaningful way is gradually becoming one of the most essential skills for succeeding in the 21st century. Accordingly, computational thinking (CT) is considered as important as the skills of reading, writing, and arithmetic. In light of this growing recognition, ACM, Code.org, Computer Science Teachers Association, Cyber Innovation Center, and National Math and Science Initiative have developed conceptual guidelines for CT education. Research developments over the last few years have proposed new pedagogies, guidelines and resources for the development of computational thinking skills. Intuitive and student-friendly computer programming environments like Alice, Scratch, BlueJay, Greenfoot, Kodu, and educational robotics, as well as new standards and guidelines from CSTA/ACM and ISTE have been widely applied. However, despite the apparent growing body of research in the area, there is limited evidence to support the design of appropriate learning experiences to allow students to adequately develop computational thinking competences.
This special issue intends to attract contributions related to innovations and technologies to support the development of CT. Research areas of particular interest include, but are not limited to:
- Psychological factors affecting the development of CT
- Adaptation and personalization in CT learning environments
- Intelligent support systems for CT
- Design of learning environments fostering CT
- Learning analytics in CT
- Informal learning experiences promoting CT
- Empirical evidence from case studies and evaluation studies ranging from K-12, to tertiary, to lifelong CT education
- Project-based learning/capstone projects in CT education
- Gender equity in CT education
- Experience with innovative pedagogies in learning or/and teaching CT
- Cognitive and metacognitive support in developing CT skills
Timeline
Paper Submission begins: October 1, 2017
End of Paper Submission: December 31, 2017
First Round of Revisions: February 2018
Revised Papers Due: April 2018
Final decisions: July 31, 2018
Anticipated Publication Date: Fall 2018
Paper submission formatting guidelines per the Journal’s Guide for Authors.
Guest editors
Charoula Angeli, Department of Education, University of Cyprus, cangeli@ucy.ac.cy
Michail Giannakos, Department of Computer Science, Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU), michailg@ntnu.no
Computers in Human Behavior – Artifact construction in Learning (submission: 30 April 2018)
Emerging Technologies for Artifact Construction in Learning
Call for Papers for a special issue for the Computers in Human Behavior titled “Emerging Technologies for Artifact Construction in Learning”
Guest Editors:
1) Dr. Antigoni Parmaxi [http://antigoniparmaxi.weebly.com/] 2) Prof. Panayiotis Zaphiris [http://www.zaphiris.com]
Cyprus Interaction Lab (http://cyprusinteractionlab.com/)
Cyprus University of Technology
Emails: antigoni.parmaxi@gmail.com; pzaphiri@cyprusinteractionlab.com
Focus of the Special Issue
The Innovating Pedagogy 2016 report claims that we are at the beginning of a learning revolution (i.e., a new era that builds and extends the impact of technology in learning in new and unanticipated ways). The goal of this special issue is to bring together different facets of emerging technologies and ground their use under the theoretical framework of constructionism. This special issue aims to include not only innovation on the use of different features of emerging technologies, but also on practices and strategies employed by practitioners and instructional designers as well as their impact on human behavior. This special issue is not constrained in the discipline of Technology-Enhanced Learning. Research on interface design, security concerns arising from the use of emerging technologies are also welcome.
Motivation for the SI
Many recent well-known successful educational activities around the world rely on emerging technologies such as social media, virtual and augmented reality, embodied technologies and mobile applications and their impact on human behavior. This special issue echoes the growing research trend towards innovations in the use of emerging technologies and makes an effort to delineate how constructionism and social constructionism ground their use. Constructionism was chosen as a theory of learning, teaching, and design that aligns well with the demands and expectations of computational culture, and emphasizes building, creating and making of shared and meaningful artifacts as a means for gaining knowledge (Papert, 1980; 1993).
Possible topics of interest
This special issue will welcome contributions on the following, though not exhaustive, list of topics:
- How can emerging technologies embody constructionist/social constructionist elements and transform educational activities?
- How can different features of emerging technologies support the construction of an artifact that can be meaningful to its constructors?
- How do learners engage in meaningful artifact construction within different emerging technologies?
- What behavioral patterns do learners display in a constructionist/social constructionist environment?
Timeline for submission:
Submission portal will be open from 15th November 2017 to 30th April 2018
Submission deadline: 30th April 2018
Author notification: September 30th, 2018
Final approval by Editor-in-chief: November 31st, 2018
Expected publication date: Early 2019
Computers in Human Behavior Journal
CHB is a Q1 Journal. It bimonthly peer-reviewed academic publish by elsevier. The most important part is CHB related to my field (HCI) and cyberpsychology (I dont know the existence of this field until today). The editor is Matthieu Guitton (Laval University, Quebec City).
In 2016, the impact factor is 3.435.
Protected: Program 1 Active Me (11 September – 22 September 2017)
Publication Process for Buku Ilmiah & Buku Karya Asli: Phase 3
Monograf — adalah buku penerbitan yang masih berbau tesis. Terma dan kandungan adalah seperti tesis. Mengandungi abstrak dan bab metodologi
Buku teks – tiada nilai penyelidikan. Boleh diambil daripada nota syarahan.
Edited volume – sama seperti research book. Cuma ada tambahan authors dalam TOC. Nama luar hanyalah nama editor sahaja.
Buku Ilmiah – ada elemen penyelidikan. Tidak berbau tesis dan sesuai untuk bacaan umum.
- Front Matter – muka judul, abstrak
- Half title page – penerbit akan buat – rekto
- title page – tajuk, nama penulis, publisher
- copyright page – verso – the back of the full title page, copyright notice, in addition most publishers, the name of the country, printing history
- dedication – optional the next right hand page – it should be simple – To my daughters with lots of love.
- acknowledgement
- epigraph – optional (kata-kata mutiara) – kata-kata Hamkha…
- table of contents – start rekto
- list of illustrations – social science or kalau tak banyak rajah maka tidak perlu.
- list of tables
- foreword (kata penghantar) – ditulis oleh orang lain. e.g pengarah, boss, menteri.
- preface – reason for writing the book, method of research and extended acknowledgements dan kepenggunaan (target audience). At least 2 page nampak cantik. Mentioned Geran, pelajar dan motivasi menghasilkan buku.
- introduction
- list of abbs
- editorial
- method
- list of contributors
- chronology/list of event
- Content – content minimum 5 chapter (perlu organize setiap chapter dan paragraph supaya sama panjang).
- Ayat simple dan senang faham. ayat pendek-pendek.
- 2-3 chapter awal tulis dengan mudah supaya orang senang faham.
- Must start with Recto – belah kanan.
- Subhead – cantik berhenti hingga level 2 sahaja.
- Reduce 1 size from text to table.
- Check type settings sehingga CRC.
- Reduce citations. cite only the important/factual
- Back Matter – references & indexed (wajib dibuat)
- Index – begins on a recto page, name and subject, entry penulis perlu sediakan.
- References
- Glossary
- Back cover – Blurb (short promotional piece) and author biodata.
- Book size – standard novel( 6×9 inches), textbook size (7×10 inches)
- Page numbering – bergantung kepada penerbit
- Typography – determines typefaces and font sizes.
- Title – pendek dan 2 lapis.
- Pages – 150 cantik untuk spine.
- Spine – author, title and publisher.
Langkah menulis
- Pre-writing – choose a topic, choose a format (ikut UTM Press), gather material, plan basic structure (from basic to go deeper 1. to 1.1. to 1.1.1)
- drafting – get your ideas on paper, use sentences and paragraph, follow the basic structure of the genre you have choosen, dont worry about getting it perfect, you can fix it later. After you finish your first draft, you should get someone to revise it – what do you like about my piece, what is unclear, what questions do you have, what do you have to improve it.
- revision – add details, examples and illustrations to strengthen and clarify. Rewrite awkward or unclear sentences or paragraphs. Cut any words that not related.
- editing = editing, correct, spelling, grammar, punctuation and style.
- publishing – Turn it in, post it to a blog, submit it to a publication, any other ideas?
- Manuscript is reviewed by appointed reviewer
Bibliografi – tak semestinya ada citation. References – mesti ada dalam citation.
Fasa 3: Perbincangan dengan Penerbit (MPWS)
- Ubah tajuk lebih santai + akademik. Buka target market postgrad untuk pasaran yang lebih luas. Jadik semua, mohon untuk cadangkan tiga tajuk – yang ada unsur santai + akademik . Tajuk aritu ialah menuju phd. Diantara tajuk yang diorang dah ada dan tak recommend kita guna ialah: 1. Hikayat seorang phd. 2. Travelog phd.
- Grafik Buku
MPWS ada designer. Once dah confirm tajuk – nanti diorang will design accordingly. - Permohonan ISBN.
Untuk dapatkan ISBN, buku perlu ada: 1. kata pendahuluan, 2. abstrak dan 3. Table of Content. Tqvm, yang ini Dr Ib dah siapkan. - Proof Read.
Terima kasih uols – kita sedang pusing proof read kan. Then bila siap nanti bagi kepada mereka, diorang akan proofread sekali lagi. - Medium Penerbitan:Pilihan 1: eBook (foc) pilihan yang diberikan kepada kita ialahterbit dalam bentuk eBook. Sebab diorang uruskan semua dan marketing pun mereka uruskan. Kos penulis ialah FOC. Keuntungan ialah 60% publisher dan 40% kita.Pilihan 2: cetak – Sekiranya hendak diterbitkan dalam bentuk buku, kadar bayaran ialah RM 1000 (kos pengurusan) + RM 4000 (kos cetak untuk 120 pages). Kos ini ditanggung oleh penulis (kira sorang dalam RM400-500 la kan). Then hak buku dan royalti semua ialah pada penulis. Kita boleh minta mereka uruskan marketing dengan cara kita jual buku kita tuh kepada mereka pula – supaya mereka boleh edarkan kepada kedai buku IPTA, MPH dan pesta bukuPilihan 3: ebook then cetak (cadangan mereka kita buat ebook dulu). Then dah siap ebook memang terus boleh cetak (kalau mahu). Sebab katanya memang begitulah cara trainer MPWS lain buat duit. Diorang jual buku diorang masa kelas dan dalam seminar.
- Tambahan kandungan setelah perbincangani. Tambah 1 bab perkahwinan/support system. Ini adalah optional contribution daripada penulis (nama sebenar tidak akan disiarkan). Bab ini akan dibuat dalam bentuk kompilasi. 1/2 – 1 page seorang. Hantar selewat-lewatnya pagi isnin ini.ii. Kesimpulan daripada perjumpaan semalam ialah teruskan mengedit – last sekali akan tiba pada saya kan? then nanti saya pas balik dan discuss dengan Dr Ib untuk softcopy. Jadi kita teruskan proses macam biasa ok, samada ebook sahaja, cetak sahaja atau ebook dan cetak – prosesnya ialah sama.iii. Keputusan untuk kaedah publication dan tajuk nanti kita buat round table – semua kena bagi pendapat untuk tajuk dan pilih kaedah publication
