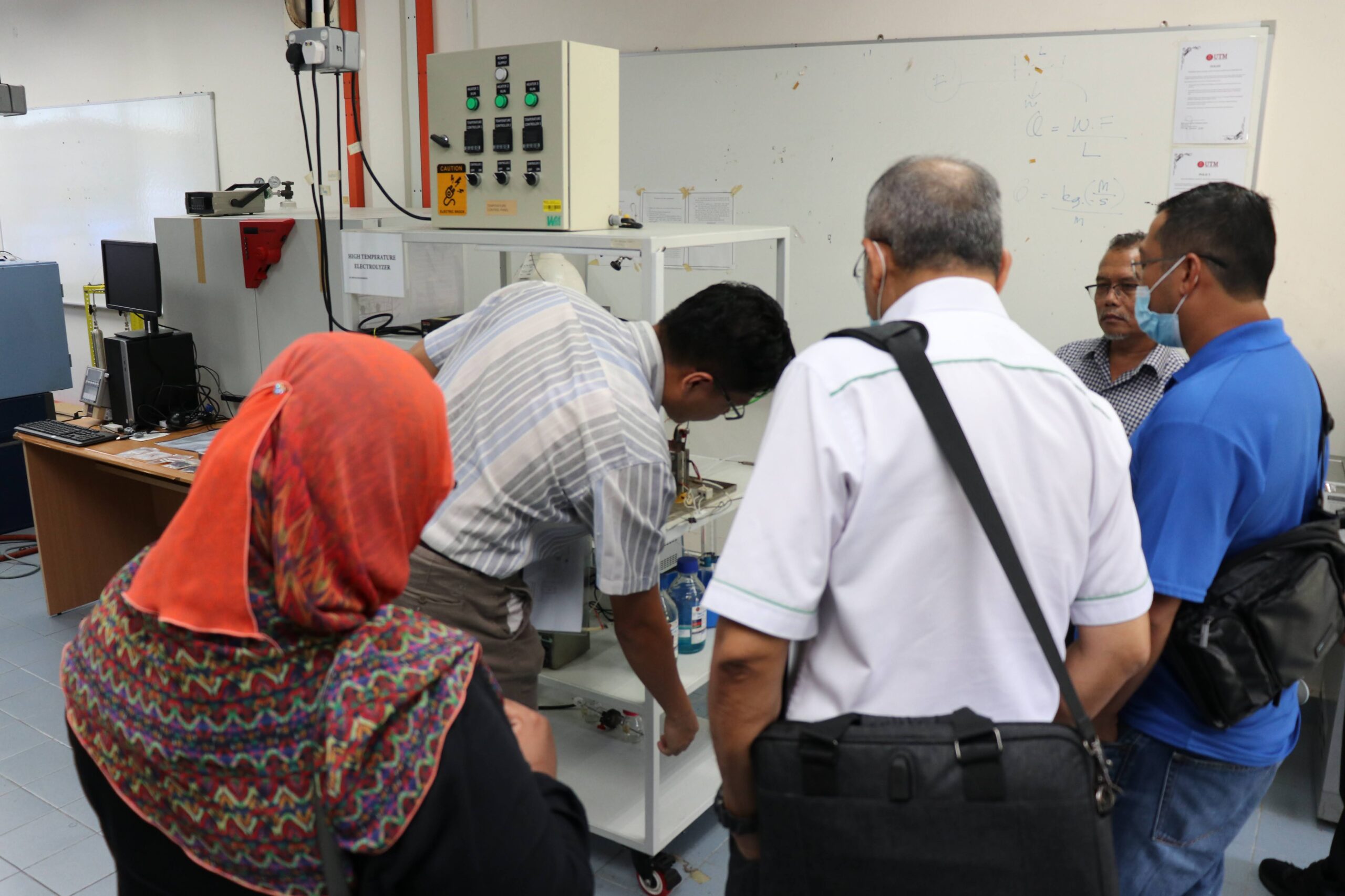
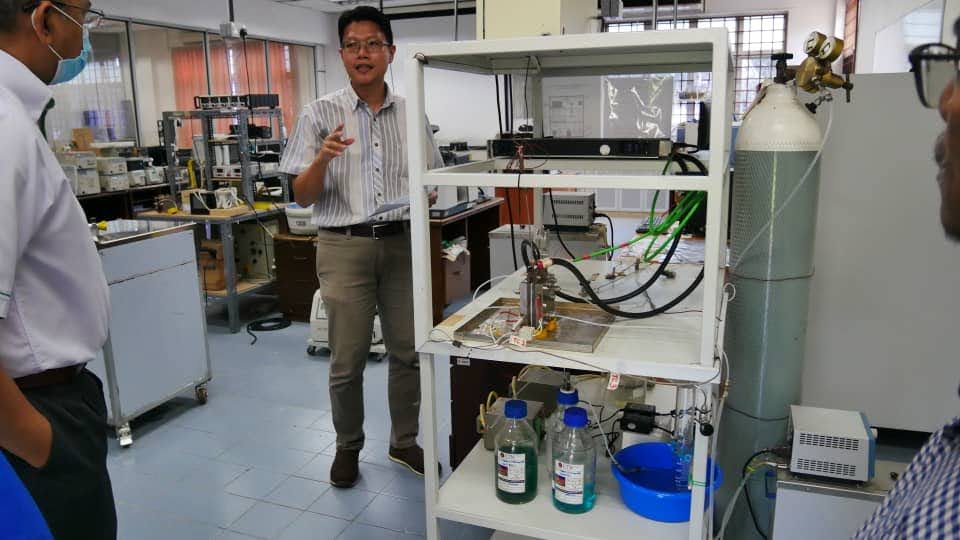
Our review article on membrane-based electrolysis for hydrogen production has been published in the Membranes Journal, Quartile 1 (Q1) with the impact factor (IF) of 4.106.
The article reviews the alkaline electrolysis and 6 types of membrane-based electrolysis for hydrogen production and its current technological progress.
The challenges and future trends were also discussed and concluded with the future developments of the cost-effective membranes for hydrogen production.
This review article is available online via open access https://lnkd.in/gNfJ84xa. Please download, share and cite the article if it is related to your research works.
https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0375/11/11/810
#membranes#electrolysis#membranebasedelectrolysis#hydrogen#hydrogenproduction#zerocarbonfootprint#watersplittingtechnologies#electrolyzer#electrolysistechnologies#research#futureenergy


 International Journal of Hydrogen Energy
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy