
In recent years, Building Information Modeling (BIM) has emerged as one of the most transformative technologies in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry. More than just a 3D modeling tool, BIM represents a digital revolution that reshapes how buildings and infrastructure are planned, designed, constructed, and maintained throughout their lifecycle.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this topic, students should be able to:
- Define the concept and principles of Building Information Modeling (BIM) and explain its significance in the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) industry.
- Describe the key components, features, and functions of BIM, including data integration, collaboration, and model management.
What is BIM?
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a process of creating and managing digital representations of physical and functional characteristics of a facility. It integrates 3D geometry, data, and collaborative workflows into a single coherent model that can be accessed and updated by all stakeholders involved in a project.
In essence, BIM serves as a shared digital platform that enables architects, engineers, contractors, and owners to collaborate more effectively. The model contains not only geometric information (the “building shape”) but also detailed data such as materials, specifications, cost estimates, schedules, and maintenance records.
The Core Concept: Information and Collaboration
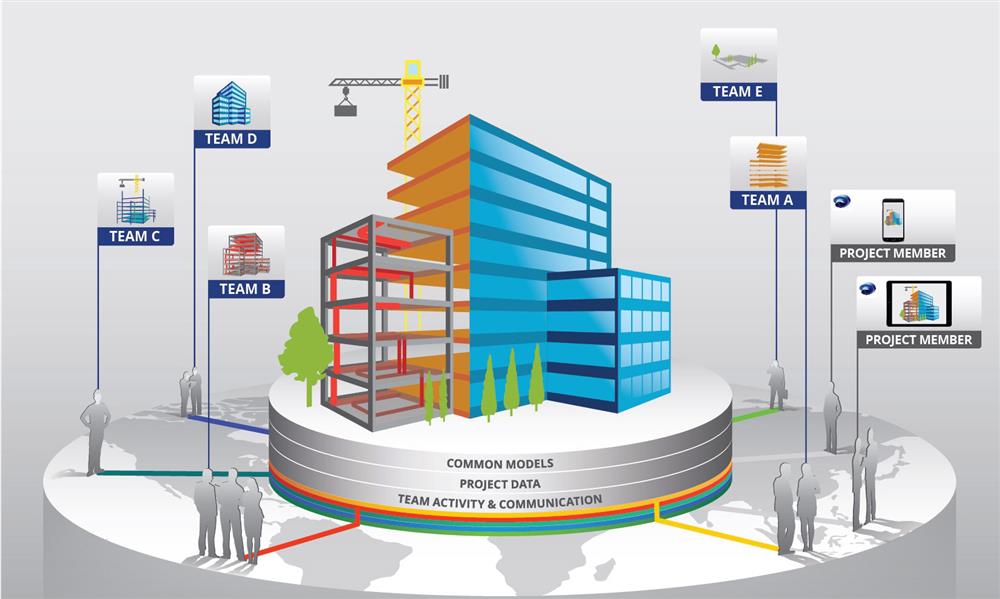
The heart of BIM lies in information management. Traditional construction drawings are often fragmented and discipline-specific, leading to miscommunication and costly errors. BIM eliminates these silos by providing a centralized database where all project information is stored and updated in real time.
When a designer modifies an element—say, changing the size of a beam—the change is automatically reflected across all relevant drawings, schedules, and cost data. This ensures consistency, accuracy, and transparency throughout the project lifecycle.
Moreover, BIM promotes collaborative decision-making, where all professionals—architects, structural and MEP engineers, quantity surveyors, and contractors—can work within a shared digital environment. This integration helps reduce conflicts, improve efficiency, and enhance overall project quality
Benefits of Implementing BIM
BIM offers numerous benefits that make it indispensable in modern construction:
1) Improved Collaboration: All stakeholders can work on the same digital model, reducing misunderstandings and design clashes.
2) Enhanced Visualization: 3D modeling helps clients and teams better understand the design before construction begins.
3) Cost and Time Savings: Early detection of errors and better coordination minimize rework and delays.
4) Lifecycle Management: BIM supports operations and maintenance by providing a digital twin of the facility.
5) Sustainability: Energy modeling and performance analysis promote greener and more efficient buildings.
