HTML Paragraphs
The HTML <p> element defines a paragraph:
Example :
<html>
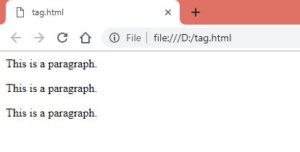
<body><p>This is a paragraph.</p>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p></body>
</html>
Output:
HTML Display
You cannot be sure how HTML will be displayed.
Large or small screens, and resized windows will create different results.
With HTML, you cannot change the output by adding extra spaces or extra lines in your HTML code.
The browser will remove any extra spaces and extra lines when the page is displayed:
Example:
<html>
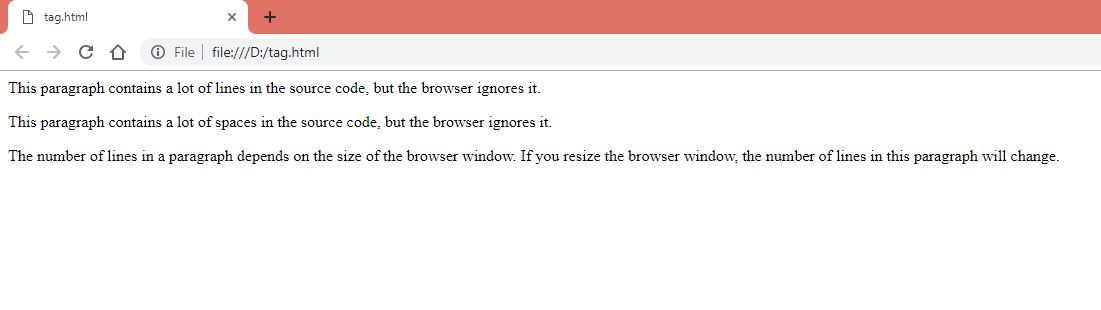
<body><p>
This paragraph
contains a lot of lines
in the source code,
but the browser
ignores it.
</p><p>
This paragraph
contains a lot of spaces
in the source code,
but the browser
ignores it.
</p><p>
The number of lines in a paragraph depends on the size of the browser window. If you resize the browser window, the number of lines in this paragraph will change.
</p></body>
</html>
Output:
HTML Line Breaks
The HTML <br> element defines a line break.
Use <br> if you want a line break (a new line) without starting a new paragraph:
Example:
<html>
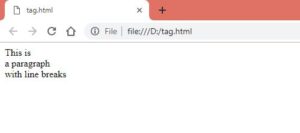
<body><p>This is<br>a paragraph<br>with line breaks</p>
</body>
</html>
Output:
The HTML <pre> Element
The HTML <pre> element defines preformatted text.
The text inside a <pre> element is displayed in a fixed-width font (usually Courier), and it preserves both spaces and line breaks:
Example:
<html>
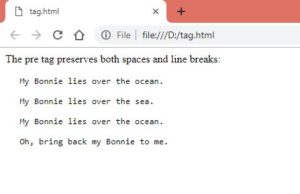
<body><p>The pre tag preserves both spaces and line breaks:</p>
<pre>
My Bonnie lies over the ocean.My Bonnie lies over the sea.
My Bonnie lies over the ocean.
Oh, bring back my Bonnie to me.
</pre></body>
</html>
Output:


Recent Comments