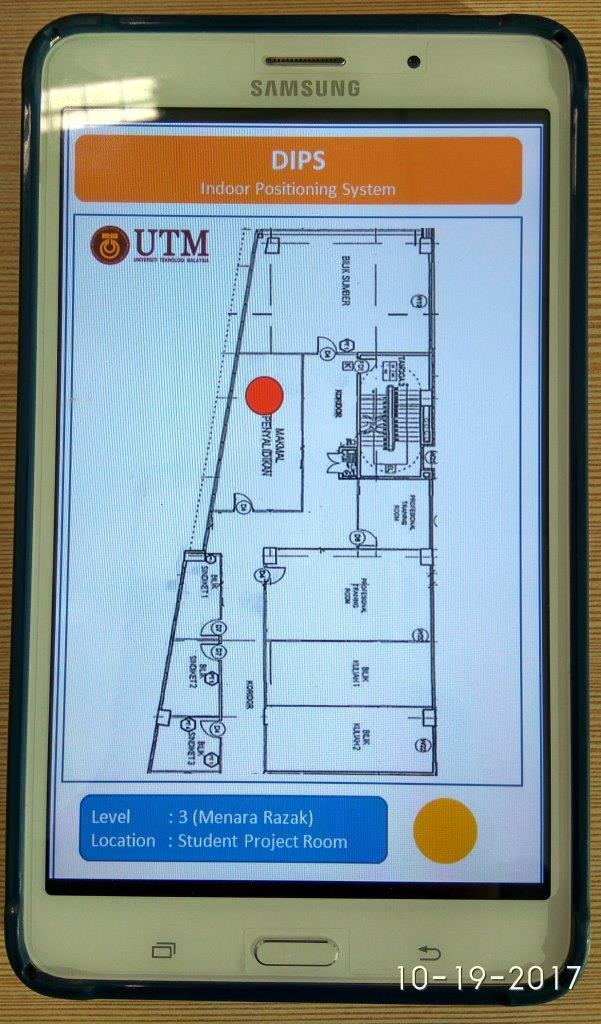
Smart Building/Campus/Hospital: Indoor Positioning Systems
The Global Positioning System demonstrates the significance of Location Based Services but it cannot be used indoors due to the lack of line of sight between satellites and receivers. Indoor Positioning Systems are needed to provide indoor Location Based Services. Wireless LAN fingerprints are one of the best choices for Indoor Positioning Systems because of their low cost, and high accuracy, however they have many drawbacks: creating radio maps is time consuming, the radio maps will become outdated with any environmental change, different mobile devices read the received signal strength (RSS) differently, and peoples’ presence in LOS between access points and mobile device affects the RSS.
Embedded Technologies for Smart Cities
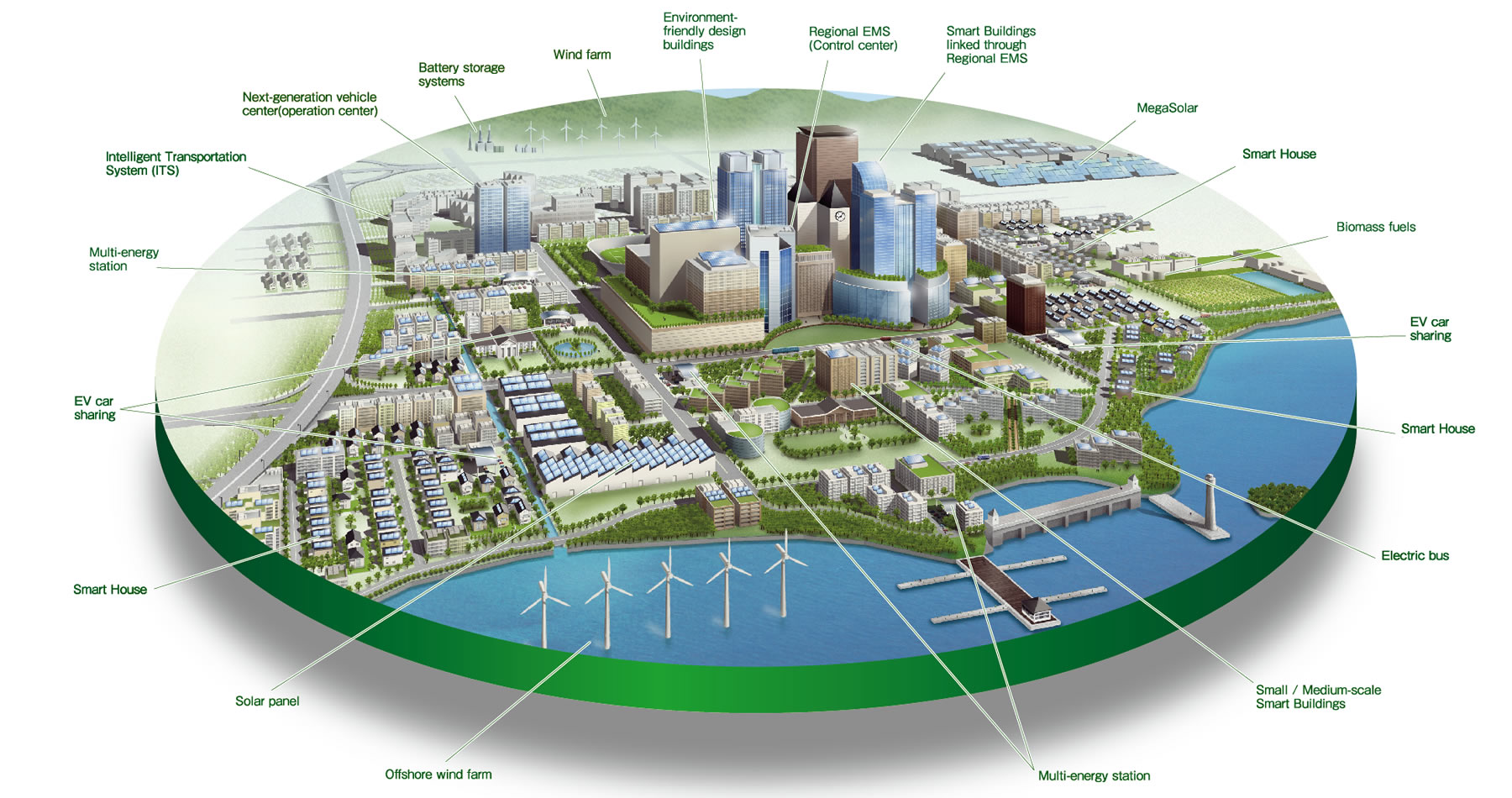
A smart city uses digital technologies to enhance performance and well-being, to reduce costs and resource consumption, and to engage more effectively and actively with its citizens. Key ‘smart’ sectors include transport, energy, health care, water and waste. A smart city should be able to respond faster to city and global challenges than one with a simple ‘transactional’ relationship with its citizens.
Cooperating Objects research areas:
- Embedded systems
- Pervasive computing systems
- Wireless sensor networks

Mixed Criticality and Real-time and Reliability in Complex Embedded Systems
The area of applications of mixed-criticality in networked complex embedded systems has been receiving increasing interest in the international research community, industry, funding agencies and policy makers. As a new field, understanding of applications and coverage of research topics have not been fully understood or identified, leaving significant gaps and establishing islands of research.Real-time designs are increasingly faced with the challenge of ensuring performance guarantees in the presence of stochastic events that lead to failures. At the same time the traditional models and techniques used to provide fault tolerance are aimed to ensure high average performance and, therefore, are inadequate for adaptation in real-time designs. One of the main aims of this session is to increase awareness about the intertwining challenges in the areas of Real-Time and Reliability.
Internet of Things
In 2013 the Global Standards Initiative on Internet of Things (IoTGSI) defined the IoT as the infrastructure of the information society. Internet of Things (IoT) as defined by the ICT (Information and Communication Technology) as a dynamic global network infrastructure with self configuring capabilities based on standard and inter operable communication protocols where physical and virtual things have identities, physical attributes and virtual personalities use intelligent interface and seamlessly integrated into the information network. IoT is the inter networking of physical devices, vehicles, buildings and other items embedded with electronics, software, sensors, actuators, and network connectivity that enable these objects to collect and exchange data. The traditional fields of embedded system, wireless sensor networks, control system, automation systems are together interconnected to form the IoT. That means the internet of things builds over the revolutionary success of mobile and internet network