Prepared by Dr. Shahabuddin Amerudin
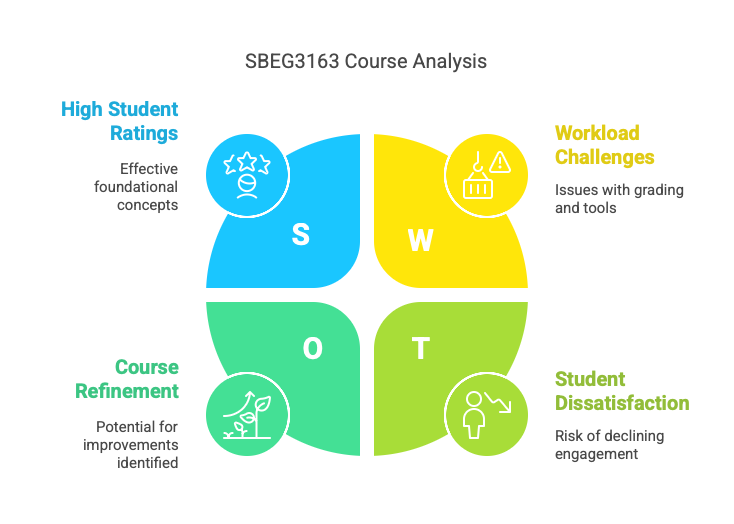
The SBEG3163 System Analysis and Design course has garnered largely positive feedback from students, reflecting its effectiveness in delivering foundational concepts while highlighting opportunities for refinement. Overall, students rated their experience an average of 4.2/5.0, with 65% awarding scores of 4.0 or higher. Many praised the course’s alignment with learning outcomes, particularly its focus on core principles such as the Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC), user requirement analysis, and practical skills like creating ERD, DFD, and UML models. However, a subset of students (20%) expressed neutrality or dissatisfaction, often citing challenges with workload management, uneven grading practices, and the complexity of technical tools.
Course Content and Structure
The curriculum was commended for its relevance to industry applications, with technical skills like database design and prototyping receiving strong ratings (4.1/5.0). Students valued hands-on projects, such as designing mockups using Adobe XD and applying CASE tools, which reinforced theoretical concepts. However, qualitative feedback revealed gaps in real-world applicability. Over 70% of respondents requested more case studies drawn from actual industry scenarios to bridge theory and practice. Additionally, some students noted that advanced topics—such as backend development, financial feasibility analysis, and system architecture—were either underemphasized or paced too quickly, leaving learners desiring deeper engagement.
Teaching Methods and Resources
Lectures and discussions were described as “engaging but demanding,” with an average rating of 4.0/5.0. Group projects and lab sessions were highlighted as strengths, fostering collaboration and critical thinking. However, reliance on pre-recorded YouTube tutorials for software training drew criticism. Students advocated for interactive, face-to-face workshops to replace passive video content, emphasizing that direct guidance would improve proficiency in tools like CASE software. One participant remarked, “Learning from videos felt isolating; live demonstrations would make complex tools less intimidating.”
Assignments and Assessments
Assignments received mixed reviews (3.8/5.0). While projects simulating real-world challenges—such as financial analyses and system prototypes—were deemed valuable, many found the workload disproportionate to allocated marks. Group projects, in particular, were cited as stressful due to uneven contributions and unclear grading criteria. Approximately 40% of students reported delays in receiving feedback, which hindered their ability to improve iteratively. Neutral or dissatisfied respondents often linked their sentiments to perceived inconsistencies in grading, with comments like, “The effort invested didn’t always reflect in the final grade.”
Technical Skill Development
Competency ratings varied across technical areas. ERD/DFD/UML modeling (4.3/5.0) and SDLC principles (4.5/5.0) emerged as strengths, with students appreciating their applicability to real-world projects. Conversely, financial feasibility analysis (3.7/5.0) and CASE tool usage (3.9/5.0) were weaker points. Many struggled with software-specific tasks, noting, “I needed more practice to confidently use these tools in professional settings.”
Student Sentiment and Recommendations
Despite critiques, 85% of students would recommend the course, underscoring its value in building skills critical to careers in geoinformatics and system design. Positive remarks highlighted the instructor’s dedication, with one student stating, “Dr. [Name]’s support and clarity made complex topics accessible.” To enhance the course, students proposed:
- Expanding hands-on training through live software workshops and industry partnerships for case studies.
- Rebalancing assignment weightings to better reflect effort and complexity.
- Providing structured, timely feedback to clarify expectations and improve learning outcomes.
- Slowing the pace for advanced modules like financial analysis and backend development.
Conclusion
The SBEG3163 course successfully equips students with essential system analysis and design skills, as evidenced by strong foundational ratings and high recommendation rates. However, targeted improvements—such as integrating real-world projects, refining grading transparency, and prioritizing interactive learning—could address current gaps. By fostering a more dynamic and applied learning environment, the course can better prepare students for the evolving demands of the tech industry while elevating overall satisfaction.