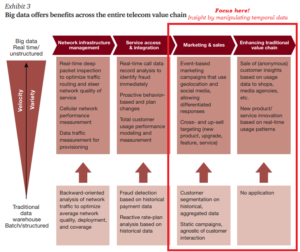
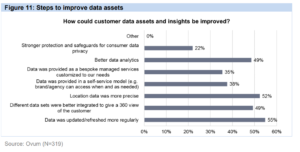
- Data monitoring activities
- What is data monitoring?
- Define monitoring
Monitoring is the verb of a monitor. Google defines it as observe and check the progress or quality of (something) over a period of time; keep under systematic review. It is also a listen and report on activities that are important to maintain regular surveillance over.Synonyms to observe, watch, track, keep an eye, keep under observation, keep watch on, surveil, record, note, oversee.From the business dictionary, it is the supervising activities in progress to ensure they are on-course and on-schedule in meeting the objectives and performance targets.
From dictionary.com, monitoring is something related to the control system that serves to remind or give warning. It is important to arrange for observing, detecting, or recording so that the activities/operation is under control. - Define data monitoring
Interesting facts from https://goo.gl/qSv9Aa, they define Monitoring as the systematic process of collecting, analyzing and using the information to track the progress of any program toward reaching its objectives and to guide management decisions. It is aligned with my thinking (please refer to my earlier post about monitoring + data temporal) when this article mentioned the relationship between monitoring activity and process (related to performance, formative evaluation?) Thus, the program indicator is relative to the progress of time (start, durations, and end). One more thing, they always relate the activity of monitoring with the evaluation. This is because, in evaluation – it is a must to provide evidence-based information that is credible, reliable and useful. Thus, through monitoring, we can provide these kinds of evidence that can lead to future findings, recommendations, and the lessons to inform future decision making.Evaluation has been defined as a systematic assessment of any activities’ performance. It focuses on expected and achieved accomplishments, examining the results chain for the whole process, its contextual factors, and causality (wow!, it means everything – from input, activities, outputs, outcomes, and impacts). They also highlight the determining of the relevance, impact, effectiveness, efficiency and sustainability interventions as the result of the evaluation (for the time being, I don’t think I can cover it all since it is too wide). - Define data monitoring activities.
- Examples of monitoring activities
- Define monitoring
- What is data monitoring?
- Assurance perspectives
- What is assurance?
- What the users want to be assured when they are doing the monitoring activities?
- Thus, from no 2 understanding – it is what we must cater when we are providing/presenting data for monitoring activities.
- In this case, let’s try focus and compare the assurance perspective from these five scenarios;
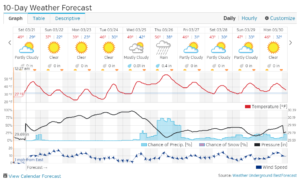
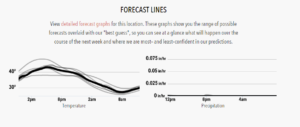
- Weather forecast
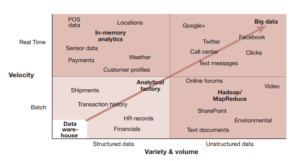
- Telco-data
- Trend analysis
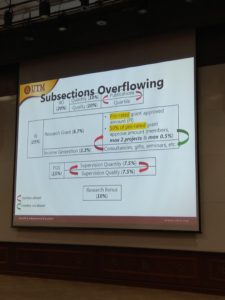
- Project management monitoring (construction)
- Data Myra monitoring
References:
- Read more: http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/monitoring.html
- Dictionary.comQuite interesting – I will read more about monitoring and evaluating on these:
- http://www.endvawnow.org/en/articles/331-why-is-monitoring-and-evaluation-important.html?next=332
- Frankel, Nina and Anastasia Gage. 2007. “M&E Fundamentals: A Self Guided Minicourse.” U.S. Agency for International Development, MEASURE Evaluation, Interagency Gender Working Group, Washington DC.
- Gage, Anastasia and Melissa Dunn. 2009. “Monitoring and Evaluating Gender-Based Violence Prevention and Mitigation Programs.” U.S. Agency for International Development, MEASURE Evaluation, Interagency Gender Working Group, Washington DC.