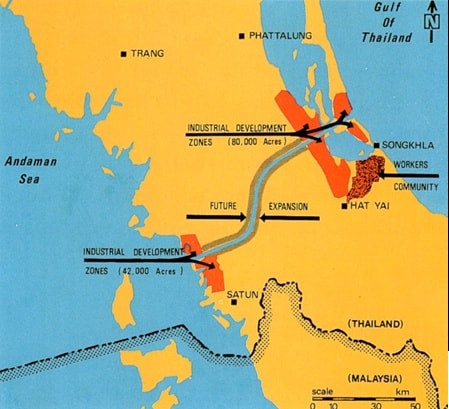
The development of industrial development zones (IDZs) in southern Thailand is poised to have a significant impact on the economic landscape of Southeast Asia, particularly for neighboring countries like Malaysia and Singapore. These zones, which are being established along the Andaman Sea coast, aim to attract foreign investment, create jobs, and stimulate economic growth in the region.
The provided image depicts a proposed development plan for the southern region of Thailand, focusing on the creation of industrial development zones along the Andaman Sea coast. The map highlights two primary zones: one near Hat Yai,covering 42,000 acres, and another in the vicinity of Songkhla, spanning 80,000 acres. The plan also outlines a future expansion of the Hat Yai zone, suggesting additional industrial development in the region.
One of the primary benefits of the IDZs is their potential to enhance regional trade and investment. By providing a conducive environment for businesses, including infrastructure, incentives, and a skilled workforce, the zones aim to foster industrialization and innovation. This could lead to increased trade between Thailand and its neighbors, as well as the development of regional supply chains, improving efficiency and reducing costs for businesses.
However, the impact of the IDZs extends beyond local economic development. The zones could also play a crucial role in reshaping maritime trade routes in Southeast Asia. By potentially creating a new shortcut for sea ships traveling between the Indian Ocean and the South China Sea, the IDZs could reduce transportation costs and time, making the region a more attractive hub for global trade. This could have far-reaching implications for the maritime industry, potentially reshaping trade patterns and economic dynamics in the region.
While the IDZs offer significant opportunities, they also present challenges. Environmental concerns, such as deforestation and pollution, must be carefully addressed to ensure sustainable development. Additionally, the concentration of industrial activities in specific areas may create social and infrastructure challenges, such as housing shortages and traffic congestion.
The success of the IDZs will depend on effective planning, implementation, and management. By addressing environmental concerns, providing adequate infrastructure, and fostering a conducive business environment, Thailand can position itself as a major player in the global maritime trade landscape. The potential benefits, both for the local economy and international trade, are significant and make this project a compelling endeavor.
For neighboring countries like Malaysia and Singapore, the IDZs present both opportunities and challenges. On the one hand, the zones could lead to increased trade and investment, as well as the development of regional supply chains. On the other hand, there may be concerns about competition for resources and talent, particularly if the IDZs focus on sectors that are already significant in these countries.
Overall, the development of the IDZs in southern Thailand has the potential to be a game-changer for Southeast Asia. By stimulating economic growth, enhancing regional trade, and reshaping maritime trade routes, the zones could significantly contribute to the prosperity and development of the region. However, it is essential to address the challenges and ensure that the IDZs are developed in a sustainable and equitable manner.