Temporal Data and Business Intelligence
According to Aigner et al (2007), time is an outstanding dimension. In popular physics, time is the fourth dimension. For ages, scientists have been thinking about meaning and implications of time. Understanding temporal relations enables us to learn from the past to predict, plan, and build the future. In the world of computerization, time is like an invisible presence. Business systems mostly operate in some sort of existential present tense and programmed into a unique timestamp, flags and update. Hence, it is no surprise that time is also a key concern in Visual Analytics, where the goal is to support the knowledge crystallization process with appropriate analytical and visual methods [1]. Visualizing time-oriented data, which is the focus of this paper, is not an easy business. Even though many approaches to this task have been published in recent years, most of them are specific to only a particular analysis problem. The reason why most methods are highly customized is simple: it is enormously difficult to consider all aspects involved when visualizing time-oriented data.
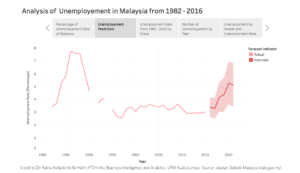
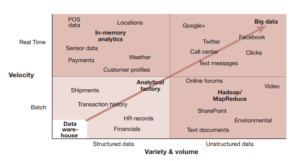
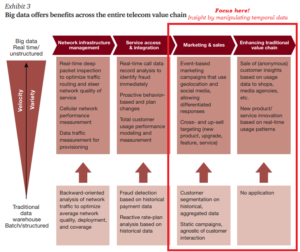
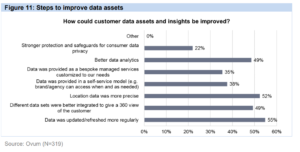
In current years, the temporal data is still valid and significant to emphasize the value of Business Intelligence (BI). The temporal concept enables business users to explore past business events to understand problems, see trends (monitor and review the data) and these activities can support the decision making as well. Thus, in many cases, users get point-in-time views of the business at defined times, such as the daily or month-end close. However, as business operations have become increasingly real-time in nature, the need for a continuous history that provides an ongoing, complete and accurate record of transactions and business performance has become paramount. Temporal — and in particular, bi-temporal — data is thus central to effective BI processes and should be a core part of any data warehouse or data mart (Devlin, BI Expert Panel)
Furthermore, the business context is growing in the complexity of both BI needs and the temporal characteristics of data. Decision making is increasingly real-time in nature. Predictive analytics extends our interest from the past and present into the future. Big data and the Internet of Things take us into a new world where the people who use data often don’t control its structure or content. Even the bi-temporal model, Johnston is reluctantly forced to admit, may turn out to be insufficient to carry all the temporal meaning that a user may wish to impart to or extract from business data. A tri-temporal model, with three-time axes, may eventually be required to make full sense of data. Then quoted from Johnson, the understanding for the interconnection between Bi, analytics and data temporal is vital if we are to navigate the expanding world of big data. Without such an understanding – Devlin believes the implementation of BI was destined to crash and burn. Therefore, it should be seen as mandatory preparation to revisit the theory and practice of temporal data.
An important issue that concerns all previous points is task-orientation. This means that Visual Analytics systems should automatically suggest and parameterize visual, analytical, and interaction methods based on the users’ task at hand. Recently, an interesting analysis of possible visualization tasks has been published in [3]. That list of tasks can be used as a basis for future research on task-oriented Visual Analytics. In that regard, perceptual issues must be further investigated. Empirical tests have to be conducted to judge which forms of presentation (2D or 3D, static or dynamic, etc.) are best suited for particular analysis tasks.
Aigner, W., Miksch, S., Müller, W., Schumann, H. and Tominski, C., 2007. Visualizing time-oriented data—a systematic view. Computers & Graphics, 31(3), pp.401-409.
Devlin, B. Temporal Data Reality: In BI, time is of the essence. https://goo.gl/VdEt7T