Protected: Envision UTMRazak Future 2020-2025
Bengkel Perancangan Strategik 2020 dan Pembangunan Pelan Jangka Panjang 2021-2025
Tarikh: 11-12 Februari 2020 (Selasa-Rabu)
Tempat: Dewan Merak, Level 2, Hotel D Palma Ampang.

- 10.30 am – Taklimat bengkel from PM Dr Suzana selaku Pengerusi Bengkel Strategik. Beliau mengharapkan percambahan idea secara profesional dalam berkongsi dan membangun peta strategik dan balance scorecared FTIR selaras dengan 6 KFA Utama UTM. Peta Strategik ini perlu dihantar pada 5 Mac 2020.
- 10.40 am – Ucapan Alu-aluan oleh Dekan. PM Dr Astuty Amrin mengingatkan untuk sama-sama bekerja lillahitaala. Semoga Allah membalas kebaikan bukan sahaja dengan 100% eLPPT tetapi juga nikmat kesihatan yang masih diberikan oleh Allah SWT.
- KFA1 Excellence in Learning and Teaching, and Transformative
Campus Experience – Diketuai oleh PM Dr Khairur Rijal – tough job untuk semakan kurikulum. - KFA 2 Research Excellence, Industry and Community Engagement – Diketuai oleh Dr Nur Azaliah Abu Bakar
- KFA 3 Sustainable Campus, Infrastructure, Information and
Communication (ICT) System – Diketuai oleh Dr Norliza Mohammad - KFA 4 Talent Transformation, Governance and High Performance
Delivery – Diketuai oleh En Nasir - KFA 5 Advancement and Business Development for Financial
Sustainability – Diketuai oleh PM Dr Nazri Mahrin – Business Center (5 entities as income generator) to get 1Mill in 2020. - KFA 6 Global Prominence and Branding – Diketuai oleh PM Dr Nor Zairah Ab Rahim.
- KFA1 Excellence in Learning and Teaching, and Transformative

3. Prof Dr Shahrin bin Mohamad (Pro Naib Canselor Strategi UTM) fokus kepada pembangunan peta strategi dan balance scorecard.
-
- Realtime short time survey.
https://www.menti.com/mgcw9bx8pc – 42 27 27. - PGU 3 2020 – UTM able to get RU within 2 years by moving to the same direction. Get more from https://www.utm.my/smo/playbook-pgu-3-2020-utm-global-plan-phase-3-2020/
- There are 5 Big Things PGU III 2020.
- The Strategy Map
- Strategic Objectives by KFA
- The Key Amal Indicators and Targets
- The High Impact Programs
- Strategic Initiatives, Action Plan or activities
- Expected Headlines
- DNA UTM (9) to ISES (Integrity, Synergy, Excellence, Sustainability).
- UTM Strategy MAP 2020 UTM-STRATEGY-MAP-2020-02012020
Add new elements S2 – UTM Core Values-Driven Talents with Great Sense of Well-being (without we realized – we are the stakeholder of UTM). Need program for togetherness, happy, cheerful and – Great Sense of Well Being. New term for 2020 is ‘work-life integration’. Previously was ‘work-life balance’. - Bayaran utilities akan ditanggung oleh fakulti. Bajet adalah daripada peruntukan mengurus.
- Kurangkan birokrasi dan processing time.
- Kenaikan pangkat perlu lebih transparen dan processing time kenaikan pangkat dimaklumkan dalam tempoh 2 tahun.
- Realtime short time survey.

4. Prof Emeritus Dato’ Ir Ts Dr Zainai bin Mohamed (fasilitator and mentor FTIR)
-
- UTM History from 1904 (Technical School), 1972 National Institute of Technology (ITK) and 1975 Universiti Teknologi Malaysia.
- New campus in Johor 1985, Idea to become RU in 2001 (wowww the main idea basically from Dato’ Zainai). In 2006, Government announce 4 Research Universiti (UM, UPM, UKM, USM) and finally from 10th June 2010 – UTM become a Research University.
- PGU History
- PGU 2012-2020. PGU 1(2012-2014), PGU 2 (2015-2017 – comprehensive) and PGU 3 (2018-2020).
- PGU 3 2020-2025 – now we are here!
- Then 6 KFA are aligned based on PGU 3.
- Standard flow to develop the strategy.
- Part 1A: Understanding the status of the Organization
- Part 1B: Understanding environment & SWOT analytsis
- Part 1C: Envisioned future, core prupsoses and core values – vision & mission.
- Part 2A …
- Key Questions to answer
- What is FTIR core business – UTM core business is teaching, research and community contributions. Then FTIR need to align and focus within it.
- Academic – Executive & Profesional Program, executive program, academic teaching for profesional, industry based academia, life-long learning.
- Research – penyelidikan dan penerbitan, solve industry problem, industrial based problem, industry driven research,
- Services – consultation, capacity building, BATC, USR
- People – prominet & experienced staff, vibrant academia,
- Discipline – multi-disciplinary, industry relevant multi-discipline.
- Keyword for FTIR
- Money concious, income generator
- Strength
- Multidisciplinary
- Strategy location – KL
- Prominent Staff – expert
- Good brand #UTMRazak & QS Ranking
- Weaknesses
- Occupational stress – too many in my plate
- Superficial synergy
- Huge skill gap
- Internal long process
- Limited internal guidelines* policy
- Poor succession planning
- low student intake for student program
- Low number of professors
- FTIR is not well branded
- Enhancing of initiatives & experts in marketing & branding
- Insufficient future ready T&L facilities
- Lack of research labs’ equipment
- Insufficient budget for outbound faculty program.
- Insufficient staff/student facilities (vending machine,
- Utilization of partnerships with other academic institutions.
- Opportunity to develop extended program beyond/after EDGE Diploma, especially for government servant (Create Bachelor program).
- Opportunities
- Leverage the social media platform available to promote FTIR.
- Propose high impact research program – based on multi-disciplinary RG.
- Threat
- Limited industry & international grants
- limited central guidelines & policy. E.g. The policy for Blockchain.
- Ranking
- Similar program within university
- Similar program from other universities
- Facilities of other (faculties, institutions and companies)
- Competitive inbound programs
- Attention to trend and Event
- Identify critical trends –
- Require Higher qualification and professional experience among sfaff,
- Require more publications and high impact/high index,
- expected more collaboartion
- more demand for life long leanring
- commercialization of academic products
- KPI-focused performance
- more services to others
- more women work force
- Exposure to entrepreneurship education
- Trade war between USA and China
- Technology transofrmation continuous to change our life – 4ir, iot, big data, blockchain, TaaS, Automation.
- Uncertainties in higher education management.
- Identify potential events (confirm berlaku) an unambigious
- Less funding for public university
- Drop in world oil price in 2016
- Coronavirus 2020.
- Forecast event and trends
- Identify critical trends –
- Market Segmentation
- Society structure in Malaysia – T20, B40, M40
- Society structure & economic sectors – e.g. elite, occupational based.
- Then focus for certain market segmentation.
- What is FTIR core business – UTM core business is teaching, research and community contributions. Then FTIR need to align and focus within it.
- Utilize Multi-discipline of FTIR in problem solving especially for social problem, grants, etc.
- Organizational Growth curve (S Curve)
- Start up zone
- Growth zone
- Transformation zone
- Addressing National Policy Issues
- RMKe 11 2006 – 2020
- RMKe 12 2021-2025
- PPPM (PT) 2015 – 2015
- Others (within UTM)
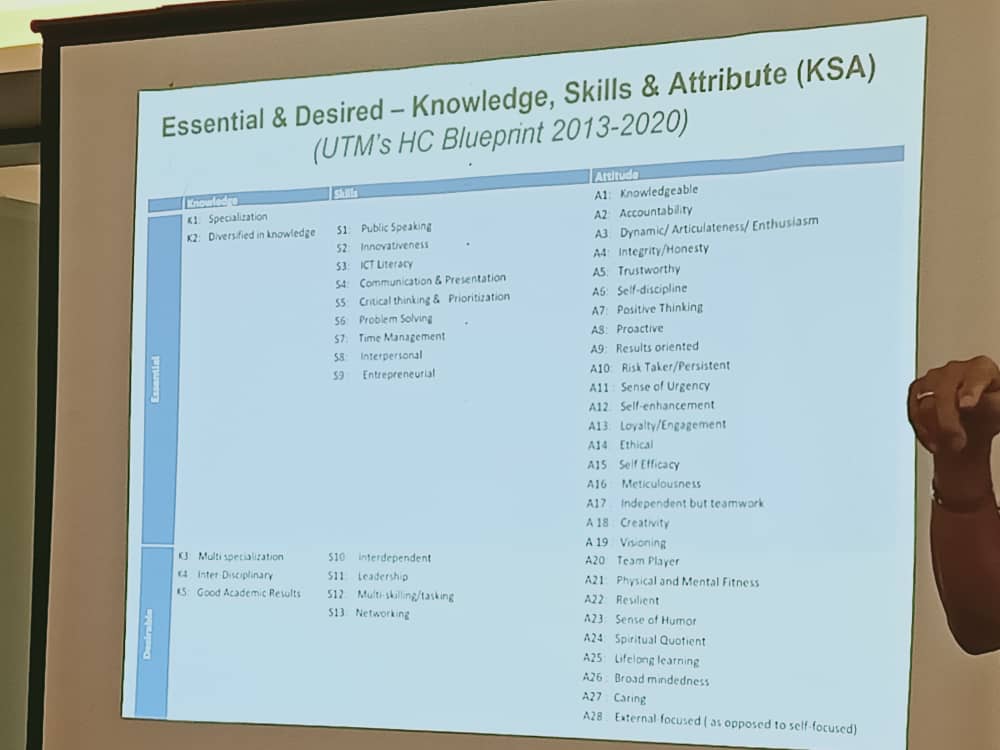
- UTM HCBP 2013 -2020 Human Capital Blue Print
- UTM Plan Global 2020 – 2025
- Essential & Desired – Knowledge, Skills & Attribute (KSA)

- Desired State (Vision/Mission)
- Strategic Management is a future-oriented
- Envisioned future – mutual & matured engagement between UTMRazak & Industries. So far only a few researchers can do this.
- core values – Realitistics.
- core purposes – Nurture the nations/Malaysia
- Strategic Management is a future-oriented
- Desired State (Vision/Mission)
How to write Good Journal
Hands on Journal Publication Workshop with Chief Editor

Hands on Journal Publication Workshop
If your research is not published in a journal it does not exist – it must be possible to find it because your paper is your passport to the community. There are 3 necessary steps in useful research:
- First is to begin with it
- Second is to end with it
- Third is to publish it
Review article (chapter 2)
Critical synthesis of a specific research topic – 8000-12,000 words
Original article
Disseminating completed research findings – 6000 – 8000 words with references. Choose the appropriate journal to build a scientific research career
TOC in Original Article
1. Title – must be catchy & spicy. Be honest & concise. the content must at par with the tittle. Make sure cover all the keyword. Less than 15 words.
2. Abstract – no technical jargon, standalone, 4W1H.
3. Keyword – repeatitive of the words so the manuscript to be easily found online and cited. should be specific, avoid uncommon abbrevieations and general terms. more than 85 repeatition should be keyword. the journal appointed reviewer based on the keywords. Not more than 5 keywords and abbs the establish one.
3. Introduction – the most difficult.
i Start by general aspect then go down to specific to your research.
ii. Flow must consistent between paragraph.
iii. Must have Statements that indicate the need for more investigation.
iv. Introduction should start with the problem in that case.
4. Study area/background (easy)
5. Methods (easy)
6. Results (easy-just the facts)
7. Discussion (second most difficult) – good paper will have good discussion.
8. Conclusions (what have done in your study) – easy. Avoid repeatition with other sections, overly speculative.
9. Acknowledgements – anyone who helped you, sources of funding. e.g. grant or reference numbers.
10. Figure 5-6 and tables 4 is appropriate. Dont put too many in one paper.
Level of difficulty
- Conference
- Non-indexed journal
- Indexed Journal
- A journal is indexed when its bibliographic and citation information is included by the citation data supplier – set turnitin similarity indexed to 0 ( I dont understand, need to check with Librarian).
- Overlapped with
- Impact factor is an annual measure of the extent to which articles in that journal are cited. It can be calculated as follows:
- Research Uni – ISI (Web of Science) and Scopus.
- ISI founded in 1960 and becoming WoS
Criteria for choosing a journal
- Scope of journal
- Indexing
- Impact factor (IF)
- number of citations that articles in the journal have received within a specific time.
-
IF=CITATIONS/ARTICLES PUBLISHED (in two years)5 year impact factor=IF in five years(sum of citations in 5 years/articles published in five years)yearly IF= IF in one year.
- Journal ranking
- Q1 & Q2 – highest quality paper
- Publication frequency
- Time to publish.
Tips to publish
- Journal selection Process
- Target 3-5 possible journal
- Choose the journal that matches the quality of journal
- Factors to consider – scope of journal, journal indexing database.

e.g. IEEE, Elsevier – high rank & top view
- http://journalfinder.elsevier.com –
- Enter title and abstract of your paper to easily find journals that could be best suited for publishing. JournalFinder uses smart search technology and field-of-research specific vocabularies to match your paper to scientific journals.
- Most downloaded papers – use it in your journal references.
- How to increase the visibility – Publish papers in somewhere pay (elsevier, IEEE) then put into researchgate so people can easily download without pay.
- Enhance your writing by:
- Critical review for thesis chapter 2 (LR)
- Finding the Gap of the study
- Novelty of the study
- Build an expertise area.
- Submitting the paper – traditional submission (email) via a journal online submission – include the cover letter (very important) – contain authors’ rationale.
- Cover letter is important. Example of cover letter:
- for choosing the editors’s journal. The letter can suggest reviewer.
- The peer review process – Editors to the reviewers to review. Then the reviewer will recommend – reject, revise, accept. Managing editor – involve in clerical and administrative detail in the review process. Makes some preliminary decisions.
- Initial screening – language, content.
- Review process from 1 hr to 6 months. 1-4 reviewers along with editorial comments. Proof preparation for checking by authors. In press/queue/article in press.
- Reviewers comment – after taking the considerations matter above – publish or reject!
- Some of the good criteria – title must be good, then get unique methods or result is something interesting, new and novelty idea.
- Addressing reviewers comment
- not being out rightly rejected
- make sure address everything
- If it is rejected – at least give some feedback
Social Network for Academic
- Research gate
- Academia Ed
- ORCID
- Google scholar
- Scopus profile Rdsearch ID profile
- Pubfacts profile
- Publons profile
Klinik Geran Universiti UTMER dan UTMFR bersama PM Dr Khairi

PM Dr Khairi share we us the importance to target for the grant. If you want 5 grants, please submit 10 proposals. He share about the grant process continuity. Make sure 1 grant will create another grant opportunities. The next grant must be better from previous grant.
Unsuccessful grant must be revised and resubmit the proposal during the next funding cycle.
Tips to write good proposal:
- How easy the reviewer to understand your proposal and how details the proposal.
- Do your background work – funding bodies, eligibility and guidelines.
- Study your funding sources
- Ensure you entitle the grant – check the guidelines for submission.
- Dont do last minute – leave plenty times
- Choose the best team for the work – need the strong team. Must be balanced – need professorship (to give advice, consel), need 1-2 associate professor and 2-4 people to do work (drs and your friends).
- Budget – provide value for money. E.g. We need the computers – then we need to justify for research usage. Printer – must be relevant to the research. Handphone – tak boleh beli – just buy for internet line. Follow the capstone. For UTM Grant – put maximum.
- Milestones – 1 year within 3-4 milestones. Follow the time duration.
UTM ER – maximum 2 years (30K for S&T) caps budget RM2million. Essential for non-PI. Insya Allah RMC will give priority to them. 2 Book chapter or research book or 1 indexed journal.
UTM FR – 2 years (70K) or 3 years (100K). Caps budget RM7.2 million. Project start date 1 November 2019. Submission deadline by 30th September 2019. Announcement of grant awarded 30 October 2019.
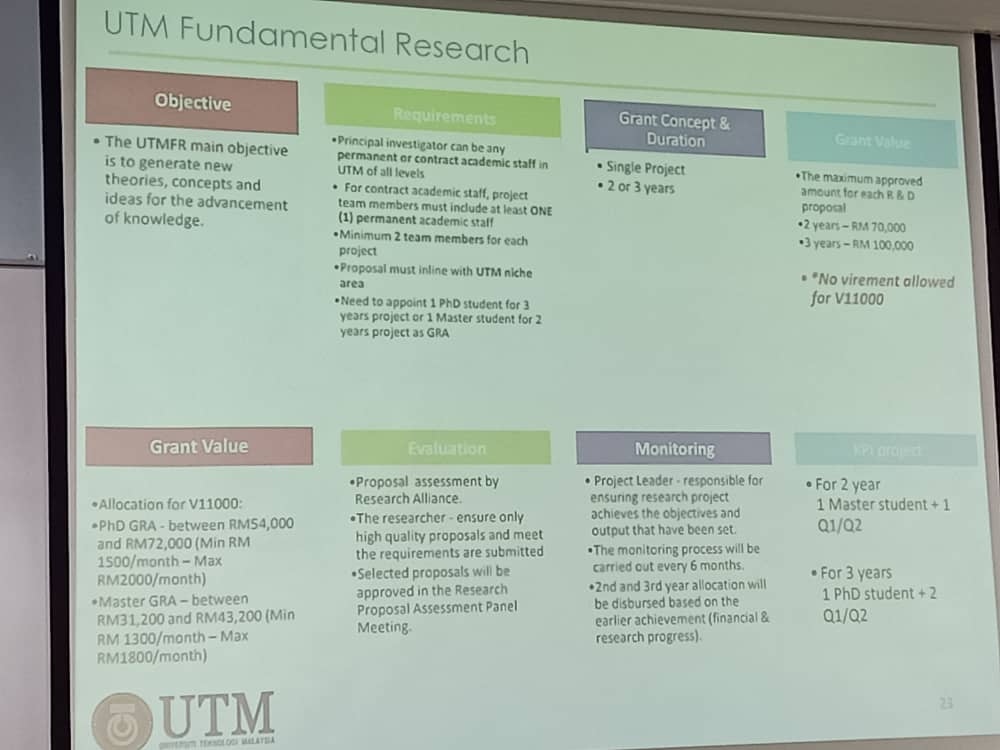
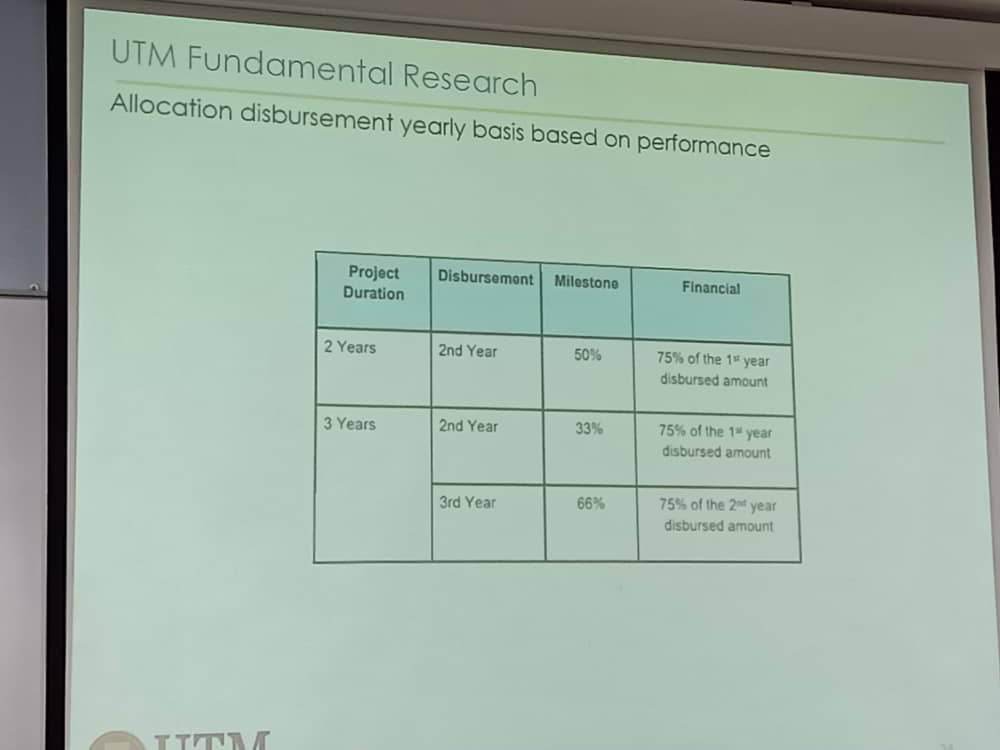
Allocation disbursement
Tips in Radis:
- Masukkan potential commercializaiton
- Collaboration proof very important to solve something.
- In the methodology masukkan;
- Flowchart perlu lebih details – nampak macam kita tau apa nak buat. The flowchart must match with the activities and objectives of the research
- Put samples –
- Research Expected result – maps with keperluan negara
- Novel theories/new findings
- Reserch publications – janjikan more and put in details where you want to publish, Indexed proceedings –
- Specific pr potential applications
- Number of phd and master by research students – put names and ID
- Impact on society, economy and nation
- Intellectual property (IP)
- Activities – 3-4 activities per year
- Equipment – patut isi – contoh komputer sedia ada dan software berkaitan. Other places – show about the collaboration.
- Budget –
- no capping. RM 1500 untuk PhD. RM18,000 x 3 tahun = RM 54,000.00.
- Q1 caps RMC RM5000.00, Q2 RM3000.00
- List and Justification – put as attachment.
Brain Games Karnival SK Hulu Klang 29 Sept 2019
Jom buat slime & jadi pilot drone ?
Ibubapa juga digalakkan untuk hadir bersama anak-anak bagi memahami konsep KBAT melalui aplikasi games dan eksperimen.
Ada lego, puzzle, wooden and soft toys untuk adik-adik 1-6 tahun.
?Mari singgah ke Brain Games Karnival SK Hulu Klang 29 Sept 2019?

Innovations in LnT: Sharing Session on NALI and AKRI Participants
Today, Prof Dr Zaidatun Tasir from Sekolah Pendidikan, Fakulti Sains Sosial dan Kemanusiaan gives talk about LnT NALI and AKRI. NALI is New Academia Learning Innovation. You can revised NALI here. AKRI is Anugerah Kecemerlangan Khas daripada Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia. This year NALI 2019 conference had been held on September 2019. Please visit here http://ctl.utm.my/nali2019/about/
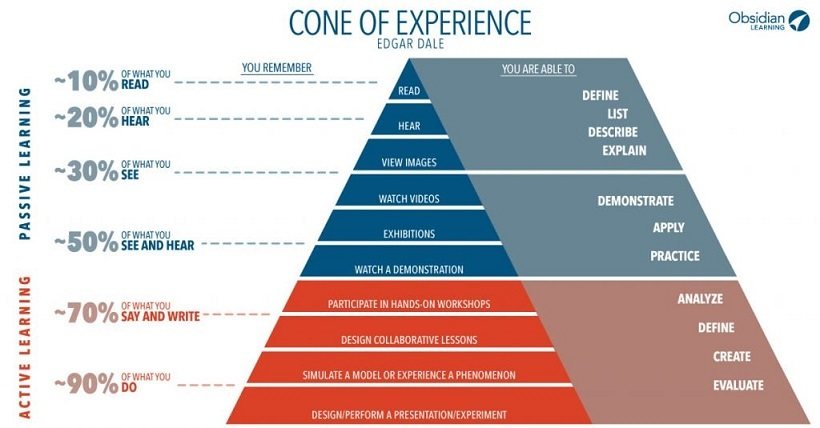
source: https://elearningindustry.com/cone-of-experience-what-really-is
Active Learning
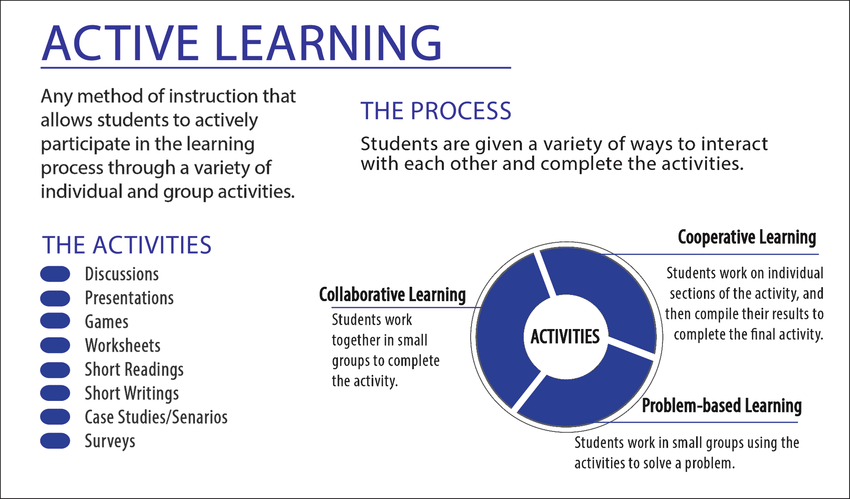
source: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Active-learning_fig1_281275352
Problem based learning – need cycle, problem formulation, weightage and assessment (triple jump). Indeed claim learning through problem or problem learning. Please visit https://www.capss.org/educational-transformation/what-are-student-centered-approaches
Students Centered Learning because four principles of
- Learning is personalized
- Students take ownership
- Learning can take time anytime and anywhere
- Competency based learning
Problem Based Learning for 21st Century Learning
- Step 1: Explore the issue.
Gather necessary information; learn new concepts, principles, and skills about the proposed topic. - Step 2: State what is known.
Individual students and groups list what they already know about the scenario and list what areas they are lacking information. - Step 3: Define the issues.
Frame the problem in a context of what is already known and information the students expect to learn. - Step 4: Research the knowledge.
Find resources and information that will help create a compelling argument - Step 5: Investigate solutions.
List possible actions and solutions to the problem, formulate and test potential hypotheses - Step 6: Present and support the chosen solution.
Clearly state and support your conclusion with relevant information and evidence. - Step 7: Review your performance.
Often forgotten, this is a crucial step in improving your problem-solving skills. Students must evaluate their performance and plan improvements for the next problem.
Learning Evolution
- Theory of Inquiry (Dewey 1938) to community of Learning
- Learning in the community – web pages, LMS, FB Groups
- Learning with the Crowd – is now 21st century learning evolution
Now learning is social network relation, interact with societies,
Crowd learning activities
New Learning theories
- Location based theory
- Space Based theory
- Constructivism theory toward connectivism in digital age (learning is a process of connecting nodes or information sources).
- https://www.educatorstechnology.com/2014/12/these-are-4-concepts-shaping-21st.html
AS104 Remote Supervision
Prof Emeritus Datuk Ir Dr Zainai Mohamed talks about AS104 – Remote Supervision at Bilik Ilmuan 1, UTM KL. Thank you SPS for arranging this session. It is superpower brain food to hear from 69 years old wise man talks about effective supervision.

Key things (foundation to understand)
- Research – original investigation undertaken in order to gain knowledge and understanding. These include curiousity-lead activity and work of direct relevance to the needs of commerce and industry.
- Scholarship – generates outputs generate
- Level of higher degree awards
- Bsc Degree Project need approx 300-400 hours with fairly demanding on level of difficulties.
- Master Degree -600-900hours
- Master Project
- Dissertation
- Thesis
- Doctor of philosophy – orginality and make some significant contribution to knowledge at least some of which might be publishable later.
- minimum of 5400 hours.
Part 1: Supervision & Effective Supervision
Supervision must be able to develop research and scholarship capability. The purpose of supervision (why):
- Share knowledge and experience.
- Guide and facilitate the students to produce research and result product.
- Enhance the student research skills
- To monitor the students within his/her study timeline. – GOT is extended monitoring – ensure the student ended at proper time.
- To motivate the students during ups and downs – not necessarily provide the solution since the motivation is itself the solution. Simple discussion, sooth them, connect them to the right people or resources is also part of the motivation.
- To facilitate research process – clarify the path for research process flow – in the reasonable scope.
Effective supervision with respect to processes.
- First of all, for effective supervision – we must know which level of degree award we supervise. e.g. for PhD, it is about supervised research training. Don’t expect the student to deliver all of your expected outcomes.
- In AS104, we are handling the student that intend to solve the real industry problem – Hence we need to carefully identify the reasonable scope and limit for this kind of situation. No need to solve the whole world, department of ministry problem within one phd.
- Develop partnership with the student. It is not only one time meeting. It is the partnership from the beginning until the end.
Expected Outcomes
- Scholarship thinking.
- Produce student with good discipline in academics
- The findings of the students research should contribute to the well being of society
- Develop research Culture and environment – and develop the culture will take sometimes.
- Develop Expertise within body of knowledge.
Part 2: Remote Supervision & Responsibilities of Participants
Remote means off campus programmes – at UTM we have: UTM Pesisir, special program, Open Distance Learning (ODL) Franchise PG Program (SPACE).
- Remote location & External student.
- Confidence in sutdent’s independency within agreed environment
- Insfrastructure – library, lab
- Expertise
- Quality assurance elements.
Take home message from Prof Emeritus Dato’ Dr Zainai to empower the supervision.
- Don’t kill the student’s ideas – accommodate the ideas.
- We are busy, but when it comes to students’ time – don’t show them we are too busy.
- Supervision is about to develop the scholarship thinking and personal abilities. To do these will take some time and partnership. Share, discuss and grow the knowledge together.
Coordinator for Masters’ Project
Dr Nilam Nur Sjarif adalah merupakan koordinator bagi semua projek master (MANB, MANQ, MANA, MANS) di Jabatan Informatik Termaju. Ini adalah jawatan baru yang akan memastikan integriti dan keadilan dalam pengagihan beban setiap penyelia.

- Registration form – Pelajar akan diberi proposal form dan mereka perlu hantar tajuk dan proposal pelajar yang ditandatangani oleh penyelia. Impak – SV in-the-know.
- Progress Report form – maksimum 4 kali pertemuan yang perlu ditandatangani – kalau lebih tiada masalah. Impak – wajib perjumpaan dengan SV.
- Consent form – minggu ke-10 perlu ada persetujuan SV untuk mengesahkan keupayaan pelajar menghantar laporan akhir.
- Minggu ke-13 untuk penghantaran laporan akhir beserta dengan turnitin.
- MInggu 14-15 lock untuk presentation project 2 dan 1.
Sesi Sua Mesra YBrs Dekan FTIR
YBrs Prof Madya Dr Astuty Amrin dilantik menjadi dekan Fakulti Teknologi dan Informatik Razak secara rasminya pada 17 Julai 2019. Berdasarkan pengalaman beliau di SPS dan akademik, dengan sokongan dua hero TDA dan TDPIPA yang gagah perkasa, insya Allah beliau menyampaikan rasa keyakinan dan besar hati untuk menerajui FTIR. Beliau adalah orang yang sangat rajin bekerja dan berintegriti. Itu adalah kekuatan utama beliau. Sekiranya beliau tidak tahu, beliau akan belajar. Sekiranya tahu beliau akan kongsi bersama orang lain.

Diantara harapan dan halatuju Razak.
- Perkasakan Sinergi 4.0.
- Kukuhkan Core Business (akademik)
- Kenaikan pangkat & succession planning
- Tingkatkan enrolmen

Alhamdulillah, Jabatan Informatik Termaju jelas perpaduannya. Itu kekuatan utama. 54% daripada staf akademik berusia antara umur 40-49 tahun. Matang dan paling produktif membuat kerja akademik, mudah pula untuk succession planning. Kepakaran setiap ahli akademik hendaklah diambil kira daripada sarjanamuda, sarjana, phd dan seterusnya bidang penyelidikan semasa yang diceburi. Jumlah pelajar penyelidikan 129 orang dan 209 pelajar baru, dekan mengingatkan para akademik untuk menyelia pelajar dengan lebih berintegriti, supportive dan bertimbangrasa. Beberapa peringatan daripada Dekan ialah:
- Pelajar kurang daripada 2 baki semester hendaklah NHT (notis hantar tesis) dengan kadar segera.
- Semester terbaik untuk Pelajar PD ialah pada semester 3.
Dekan Do’s
1. Profesionalism & Disiplin – waktu kerja, cara berpakaian, peraturan mengguna kenderaan dan arahan bertukar bilik.
2. Etika & integriti – AP59, etika sosial, menjaga nama baik Fakulti dan UTM, kepakaran yang sebenar.
Dekan Dont’s
1. Penyebaran maklumat tidak benar.