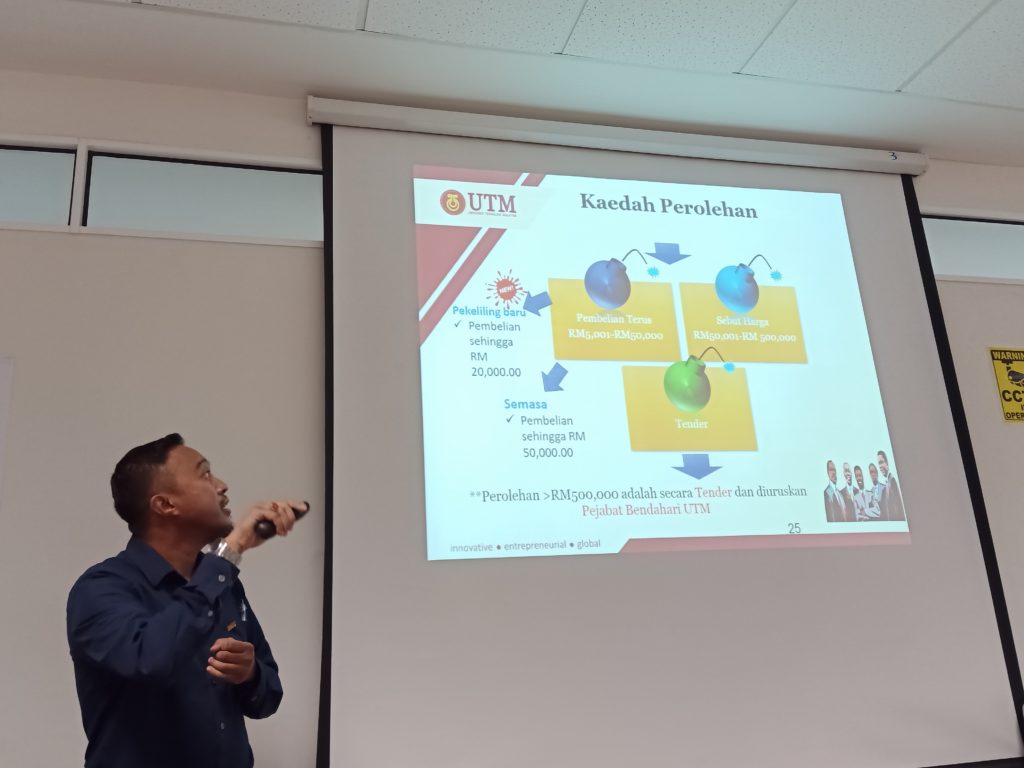
On 11 July 2019 (Wednesday), Dr Nihra share with us about Teaching Excellency System (TES). Basically TES is about compilation for our teaching development. For kenaikan pangkat, the lecturer must get DCP bend more than 2.33 for VK7 and bend more than 2.1 for DS54. You can access TES through my.utm.my on academic module.
For individual, we can access our academic profile through academic.utm.my/academician/dashboard.aspx (my.utm.my/academic)Annual Learning boleh akses sini (https://caps.utm.my) -> hanya bos sahaja boleh akses ye (coordinator – in Razak Faculty Dr Syahid).

Basically there are two elements within TES – teaching portfolio (as a platform untuk maklumat pencapaian serta keupayaan staf akademik untuk menguasai kompetensi asas (KA) dan kompetensi dibezakan (KD) dalam pengajaran dan pembelajaran. Another one is about a platform untuk memasukkan penilaian pengajaran daripada pakar dan rakan setugas bagi tujuan kenaikan pangkat. Terdapat 7 modul dalam TES iaitu:

Module 1 – Blended Learning.
Sila rujuk sini untuk faham eLearning
Module 2 – OBE.
OBE lebih lanjut sila rujuk sini
- CAR buat Manual – hantar kepada KJ
- Buat melalui sistem – Course Analysis using OBE (http://obe.utm.my)
Module 3 – NALI HIEPS
Sila klik sini untuk faham HIEPS
atau klik sini untuk faham tentang active learning
- Tanya student (access from ePPP) – ditanya daripada 3 perspektif – penyampaian, generic skill dan NALI. Selalunya pelajar tak berapa paham – so I need to explain to students every semester during the course.
- Dapatkan evidence daripada pensyarah (upload ke sistem)
Module 4 – Teaching Using Technology
Sila klik sini untuk faham teachning and technology
atau klik sini untuk mengetahui lebih lanjut tentang active learning dengan penggunaan technology
Module 5 – eCONTENT (e-kandungan asli terbuka) bonus for eLPPT
Boleh guna teknologi seperti di atas untuk membangunkan e-Content
Syarat diterima sebagai e-Content:
- Perlu dibangunkan sendiri oleh pensyarah.
- Tidak melanggar copyright license
- perlu open (online and can be access to everyone) – wordpress, youtube, padlets, facebook cannot only friends.
- Boleh apply untuk markah eLPPT melalui online……
- Tahap bahan kandungan
- Reseptif – pelajar hanya menerima kandungan pengajaran – 1 marks. e.g. pdf, teks, ppt yang pelajar boleh download sahaja.
- Interactive dalaman antara pelajar dan komputer – 2 markah
- Ada ciri sumbangsaran-5marks
- Mestilah education content/learning
- can – video during our class
- cannot be tazkirah, consultation, teaser bengkel dsb
- cannot be double count (already got in eLearning – hence eLearning UTM )
Module 6 – Teaching Portfolio (modul 6) – end date July 2019 [new!!!]
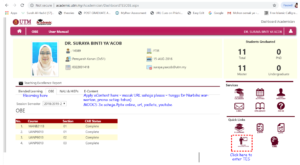
Teaching portfolio – myutm UTMACAD > TESDCP
Idea asal daripada Royal Academy of Engineering

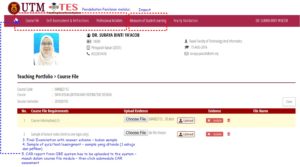
- Teaching Portfolio Course File (CAR File) – masukkan every semester (start this semester by July 2019). Masukkan CAR according to these:
- Self-Assessment & Reflection (upload sekali sahaja setahun – mptambil contoh daripada elearning Dr Nihra & benchmark based on rubrics yanng disediakan (Bend 1- Bend 4) – peringatan untuk key-in within 20 minutes duration before timeout.
- Professional Activities. Tarik from system. At least 40 credits untuk kenaikan pangkat.
- Formal professional activities -Appointed as teaching speaker, appointed as expert panel related to that subject.
- Informal professional activities – need to do report –
- boleh guna pptx or docs untuk explain semua activities yang dijalankan. e.g. Dr Nihra used flipgrid (untuk flipclassroom) and show the evidence – activities, pictures, certificate involved.
- Siapa rajin menulis sila buat karangan like teaching methodology – explain all about class session, active learning, dsb.
- Testimony and testimony (from others) – IMPACT
- Measures of student learning – feedback and testimony. Gambar, makan, dsb.
Module 7 – Teaching Observation
Need more info for this.